Autonomy for the Swazis of southern Africa was guaranteed by the British in the late 19th century; independence was granted in 1968. Student and labor unrest during the 1990s pressured King MSWATI III, the world's last absolute monarch, to grudgingly allow political reform and greater democracy, although he has backslid on these promises in recent years. A constitution came into effect in 2006, but political parties remain banned. The African United Democratic Party tried unsuccessfully to register as an official political party in mid 2006. Talks over the constitution broke down between the government and progressive groups in 2007. Swaziland recently surpassed Botswana as the country with the world's highest known HIV/AIDS prevalence rate.
Population
1,354,051
Country comparison to the world:152
note:estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2010 est.)
Nationality
Noun:Swazi(s)
Adjective:Swazi
Ethnic groups
African 97%, European 3%
Religions
Zionist 40% (a blend of Christianity and indigenous ancestral worship), Roman Catholic 20%, Muslim 10%, other (includes Anglican, Bahai, Methodist, Mormon, Jewish) 30%
Languages
English (official, government business conducted in English), siSwati (official)
Country Name
Conventional long form:Kingdom of Swaziland
Conventional short form:Swaziland
Local long form:Umbuso weSwatini
Local short form:eSwatini
Government Type
monarchy
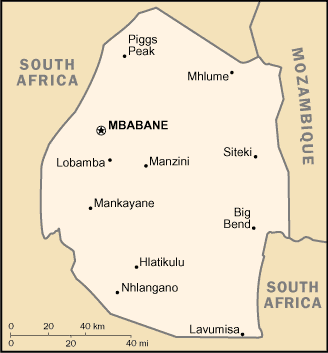
Capital
Name:Mbabane
Geographic coordinates:26 18 S, 31 06 E
Time difference:UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
note: Lobamba (royal and legislative capital)
Administrative divisions
4 districts; Hhohho, Lubombo, Manzini, Shiselweni
Independence
6 September 1968 (from the UK)
National Holiday
Independence Day, 6 September (1968)
Constitution
signed by the King in July 2005; went into effect on 8 February 2006
Legal system
based on South African Roman-Dutch law in statutory courts and Swazi traditional law and custom in traditional courts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
Suffrage
18 years of age
Executive branch
Chief of state:King MSWATI III (since 25 April 1986)
Head of government:Prime Minister Barnabas Sibusiso DLAMINI (since 16 October 2008)
Cabinet:Cabinet recommended by the prime minister and confirmed by the monarch
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections: the monarchy is hereditary; prime minister appointed by the monarch from among the elected members of the House of Assembly
Legislative branch
bicameral Parliament or Libandla consists of the Senate (30 seats; 10 members appointed by the House of Assembly and 20 appointed by the monarch; members to serve five-year terms) and the House of Assembly (65 seats; 10 members appointed by the monarch and 55 elected by popular vote; members to serve five-year terms)
Elections:House of Assembly - last held on 19 September 2008 (next to be held in 2013)
Election results:House of Assembly - balloting is done on a nonparty basis; candidates for election nominated by the local council of each constituency and for each constituency the three candidates with the most votes in the first round of voting are narrowed to a single winner by a second round
Judicial branch
High Court; Supreme Court; judges for both courts are appointed by the monarch
Political Parties and Leaders
the status of political parties, previously banned, is unclear under the 2006 Constitution and currently being debated; the following are considered political associations; African United Democratic Party or AUDP [Stanley MAUNDZISA, president]; Imbokodvo National Movement or INM; Ngwane National Liberatory Congress or NNLC [Obed DLAMINI, president]; People's United Democratic Movement or PUDEMO [Mario MASUKU, president]
Political pressure groups and leaders
Swaziland Federation of Trade Unions; Swaziland and Solidarity Network or SSN
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, COMESA, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PCA, SACU, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Ephraim Mandlenkosi M. HLOPHE
Chancery:1712 New Hampshire Avenue, NW, Washington, DC 20009
Telephone:[1] (202) 234-5002
FAX:[1] (202) 234-8254
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Earl M. IRVING
Embassy:2350 Mbabane Place, Mbabane
Mailing address:P. O. Box 199, Mbabane
Telephone:[268] 404-2445
FAX:[268] 404-2059
Flag description
three horizontal bands of blue (top), red (triple width), and blue; the red band is edged in yellow; centered in the red band is a large black and white shield covering two spears and a staff decorated with feather tassels, all placed horizontally; blue stands for peace and stability, red represents past struggles, and yellow the mineral resources of the country; the shield, spears, and staff symbolize protection from the country's enemies, while the black and white of the shield are meant to portray black and white people living in peaceful coexistence