Since independence from Portugal in 1974, Guinea-Bissau has experienced considerable political and military upheaval. In 1980, a military coup established authoritarian dictator Joao Bernardo 'Nino' VIEIRA as president. Despite setting a path to a market economy and multiparty system, VIEIRA's regime was characterized by the suppression of political opposition and the purging of political rivals. Several coup attempts through the 1980s and early 1990s failed to unseat him. In 1994 VIEIRA was elected president in the country's first free elections. A military mutiny and resulting civil war in 1998 eventually led to VIEIRA's ouster in May 1999. In February 2000, a transitional government turned over power to opposition leader Kumba YALA after he was elected president in transparent polling. In September 2003, after only three years in office, YALA was ousted by the military in a bloodless coup, and businessman Henrique ROSA was sworn in as interim president. In 2005, former President VIEIRA was re-elected president pledging to pursue economic development and national reconciliation; he was assassinated in March 2009. Malam Bacai SANHA was elected in an emergency election held in June 2009.
Population
1,565,126 (July 2010 est.)
Country comparison to the world:150
Nationality
Noun:Guinean(s)
Adjective:Guinean
Ethnic groups
African 99% (includes Balanta 30%, Fula 20%, Manjaca 14%, Mandinga 13%, Papel 7%), European and mulatto less than 1%
Religions
Muslim 50%, indigenous beliefs 40%, Christian 10%
Languages
Portuguese (official), Crioulo, African languages
Country Name
Conventional long form:Republic of Guinea-Bissau
Conventional short form:Guinea-Bissau
Local long form:Republica da Guine-Bissau
Local short form:Guine-Bissau
Former:Portuguese Guinea
Government Type
republic
Capital
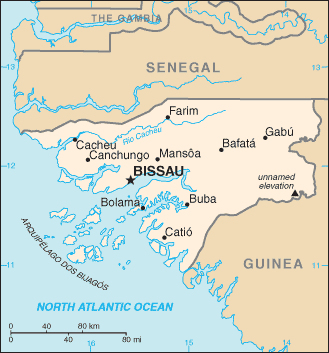
Name: Bissau
Geographic coordinates: 11 51 N, 15 35 W
Time difference:UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
Administrative divisions
9 regions (regioes, singular - regiao); Bafata, Biombo, Bissau, Bolama, Cacheu, Gabu, Oio, Quinara, Tombali; note - Bolama may have been renamed Bolama/Bijagos
Independence
24 September 1973 (declared); 10 September 1974 (from Portugal)
National Holiday
Independence Day, 24 September (1973)
Constitution
16 May 1984; amended 4 May 1991, 4 December 1991, 26 February 1993, 9 June 1993, and in 1996
Legal system
based on French civil law; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state:President Malam Bacai SANHA (since 8 September 2009)
Head of government:Prime Minister Carlos GOMES Junior (since 25 December 2008)
Cabinet: NA
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (no term limits); election last held on 28 June 2009 with a runoff between the two leading candidates held on 26 July 2009 (next to be held by 2014); prime minister appointed by the president after consultation with party leaders in the legislature
Election results: Malam Bacai SANHA elected president; percent of vote, second ballot - Malam Bacai SANHA 63.5%, Kumba YALA 36.5%
Legislative branch
unicameral National People's Assembly or Assembleia Nacional Popular (100 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
Elections:last held on 16 November 2008 (next to be held in 2012)
Election results:percent of vote by party - PAIGC 49.8%, PRS 25.3%, PRID 7.5%, PND 2.4%, AD 1.4%, other parties 13.6%; seats by party - PAIGC 67, PRS 28, PRID 3, PND 1, AD 1
Judicial branch
Supreme Court or Supremo Tribunal da Justica (consists of nine justices appointed by the president and serve at his pleasure; final court of appeals in criminal and civil cases); Regional Courts (one in each of nine regions; first court of appeals for Sectoral Court decisions; hear all felony cases and civil cases valued at more than $1,000); 24 Sectoral Courts (judges are not necessarily trained lawyers; they hear civil cases valued at less than $1,000 and misdemeanor criminal cases)
Political Parties and Leaders
African Party for the Independence of Guinea-Bissau and Cape Verde or PAIGC [Carlos GOMES Junior]; Democratic Alliance or AD [Victor MANDINGA]; Democratic Social Front or FDS [Rafael BARBOSA]; Electoral Union or UE [Joaquim BALDE]; Guinea-Bissau Civic Forum/Social Democracy or FCGSD [Antonieta Rosa GOMES]; Guinea-Bissau Democratic Party or PDG; Guinea-Bissau Socialist Democratic Party or PDSG [Serifo BALDE]; Labor and Solidarity Party or PST [Lancuba INDJAI]; New Democracy Party or PND; Party for Democratic Convergence or PCD [Victor MANDINGA]; Party for Renewal and Progress or PRP; Party for Social Renewal or PRS [Kumba YALA]; Progress Party or PP; Republican Party for Independence and Development or PRID [Aristides GOMES]; Union of Guinean Patriots or UPG [Francisca VAZ]; Union for Change or UM [Amine SAAD]; United Platform or UP (coalition formed by PCD, FDS, FLING, and RGB-MB); United Popular Alliance or APU; United Social Democratic Party or PUSD [Frnacisco FADUL]
Political pressure groups and leaders
NA
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AOSIS, AU, CPLP, ECOWAS, FAO, FZ, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OIF, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (regional), WAEMU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:none; note - Guinea-Bissau does not have official representation in Washington, DC
Diplomatic representation from the US
the US Embassy suspended operations on 14 June 1998 in the midst of violent conflict between forces loyal to then President VIEIRA and military-led junta; the US Ambassador to Senegal is accredited to Guinea-Bissau
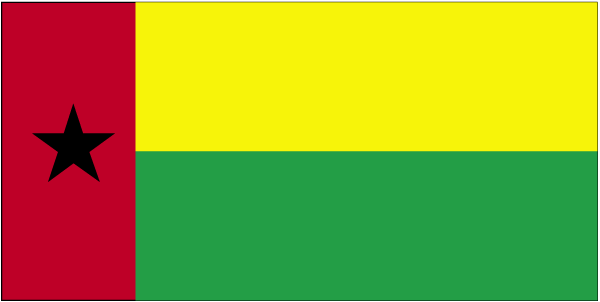
Flag description
two equal horizontal bands of yellow (top) and green with a vertical red band on the hoist side; there is a black five-pointed star centered in the red band
note: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia