As Europe's largest economy and second most populous nation (after Russia), Germany is a key member of the continent's economic, political, and defense organizations. European power struggles immersed Germany in two devastating World Wars in the first half of the 20th century and left the country occupied by the victorious Allied powers of the US, UK, France, and the Soviet Union in 1945. With the advent of the Cold War, two German states were formed in 1949: the western Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) and the eastern German Democratic Republic (GDR). The democratic FRG embedded itself in key Western economic and security organizations, the EC, which became the EU, and NATO, while the Communist GDR was on the front line of the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact. The decline of the USSR and the end of the Cold War allowed for German unification in 1990. Since then, Germany has expended considerable funds to bring Eastern productivity and wages up to Western standards. In January 1999, Germany and 10 other EU countries introduced a common European exchange currency, the euro.
Country Name
Conventional long form:Federal Republic of Germany
Conventional short form:Germany
Local long form:Bundesrepublik Deutschland
Local short form:Deutschland
Former:German Empire, German Republic, German Reich
Government Type
federal republic
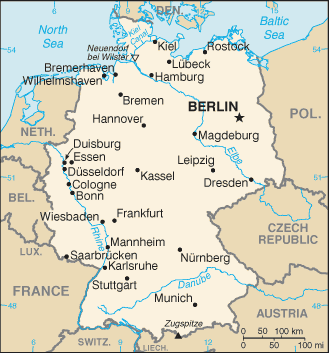
Capital
Name:Berlin
Geographic coordinates:52 31 N, 13 24 E
Time difference:UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
Administrative divisions
16 states (Laender, singular - Land); Baden-Wurttemberg, Bayern (Bavaria), Berlin, Brandenburg, Bremen, Hamburg, Hessen, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania), Niedersachsen (Lower Saxony), Nordrhein-Westfalen (North Rhine-Westphalia), Rheinland-Pfalz (Rhineland-Palatinate), Saarland, Sachsen (Saxony), Sachsen-Anhalt (Saxony-Anhalt), Schleswig-Holstein, Thuringen (Thuringia); note - Bayern, Sachsen, and Thuringen refer to themselves as free states (Freistaaten, singular - Freistaat)
Independence
18 January 1871 (German Empire unification); divided into four zones of occupation (UK, US, USSR, and later, France) in 1945 following World War II; Federal Republic of Germany (FRG or West Germany) proclaimed 23 May 1949 and included the former UK, US, and French zones; German Democratic Republic (GDR or East Germany) proclaimed 7 October 1949 and included the former USSR zone; West Germany and East Germany unified 3 October 1990; all four powers formally relinquished rights 15 March 1991
National Holiday
Unity Day, 3 October (1990)
Constitution
23 May 1949, known as Basic Law; became constitution of the united Germany 3 October 1990
Legal system
civil law system with indigenous concepts; judicial review of legislative acts in the Federal Constitutional Court; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state:President Horst KOEHLER (since 1 July 2004)
Head of government:Chancellor Angela MERKEL (since 22 November 2005)
Cabinet:Cabinet or Bundesminister (Federal Ministers) appointed by the president on the recommendation of the chancellor
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:president elected for a five-year term (eligible for a second term) by a Federal Convention, including all members of the Federal Assembly and an equal number of delegates elected by the state parliaments; election last held on 23 May 2009 (next scheduled for 23 May 2014); chancellor elected by an absolute majority of the Federal Assembly for a four-year term; Bundestag vote for Chancellor last held after 27 September 2009 (next to follow the legislative election to be held no later than 2013)
Election results:Horst KOEHLER reelected president; received 613 votes of the Federal Convention against 503 for Gesine SCHWAN; Angela MERKEL reelected chancellor; vote by Federal Assembly 323 to 285 with four abstentions
Legislative branch
bicameral legislature consists of the Federal Council or Bundesrat (69 votes; state governments sit in the Council; each has three to six votes in proportion to population and are required to vote as a block) and the Federal Assembly or Bundestag (622 seats; members elected by popular vote for a four-year term under a system of personalized proportional representation; a party must win 5% of the national vote or three direct mandates to gain proportional representation and caucus recognition)
Elections: Bundestag - last held on 27 September 2009 (next to be held no later than autumn 2013); note - there are no elections for the Bundesrat; composition is determined by the composition of the state-level governments; the composition of the Bundesrat has the potential to change any time one of the 16 states holds an election
Election results: Bundestag - percent of vote by party - CDU/CSU 33.8%, SPD 23%, FDP 14.6%, Left 11.9%, Greens 10.7%, other 6%; seats by party - CDU/CSU 239, SPD 146, FDP 93, Left 76, Greens 68
Judicial branch
Federal Constitutional Court or Bundesverfassungsgericht (half the judges are elected by the Bundestag and half by the Bundesrat)
Political Parties and Leaders
Alliance '90/Greens [Claudia ROTH and Cem OZDEMIR]; Christian Democratic Union or CDU [Angela MERKEL]; Christian Social Union or CSU [Horst SEEHOFER]; Free Democratic Party or FDP [Guido WESTERWELLE]; Left Party or Die Linke [Lothar BISKY and Oskar LAFONTAINE]; Social Democratic Party or SPD [Sigmar GABRIEL]
Political pressure groups and leaders
business associations and employers' organizations; trade unions; religious, immigrant, expellee, and veterans groups
International organization participation
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council (observer), Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS, CDB, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-20, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, Schengen Convention, SECI (observer), SICA (observer), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (nonregional), WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission: Ambassador Klaus SCHARIOTH
Chancery:4645 Reservoir Road NW, Washington, DC 20007
Telephone:[1] (202) 298-4000
FAX:[1] (202) 298-4249
Consulate(s) general:Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, San Francisco
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Philip D. MURPHY
Embassy:Pariser Platz 2, 14191 Berlin; note - new embassy opened 4 July 2008
Mailing address: PSC 120, Box 1000, APO AE 09265, Clayallee 170, 14195 Berlin
Telephone:[49] (030) 2385174
FAX:[49] (030) 8305-1215
consulate(s) general: Duesseldorf, Frankfurt am Main, Hamburg, Leipzig, Munich
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of black (top), red, and gold; these colors have played an important role in German history and can be traced back to the medieval banner of the Holy Roman Emperor - a black eagle with red claws and beak on a gold field