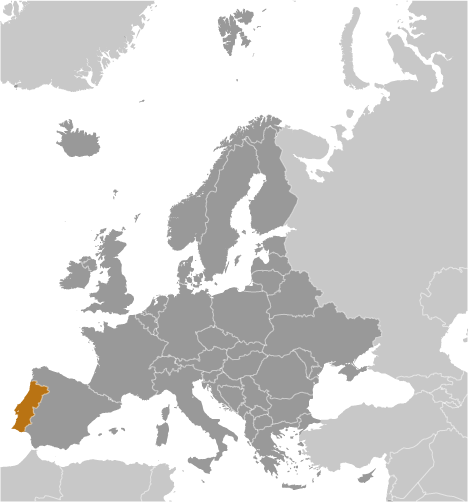
Following its heyday as a global maritime power during the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal lost much of its wealth and status with the destruction of Lisbon in a 1755 earthquake, occupation during the Napoleonic Wars, and the independence of its wealthiest colony of Brazil in 1822. A 1910 revolution deposed the monarchy; for most of the next six decades, repressive governments ran the country. In 1974, a left-wing military coup installed broad democratic reforms. The following year, Portugal granted independence to all of its African colonies. Portugal is a founding member of NATO and entered the EC (now the EU) in 1986.
Country Name
Conventional long form:Portuguese Republic
Conventional short form:Portugal
Local long form:Republica Portuguesa
Local short form:Portugal
Government Type
republic; parliamentary democracy
Capital
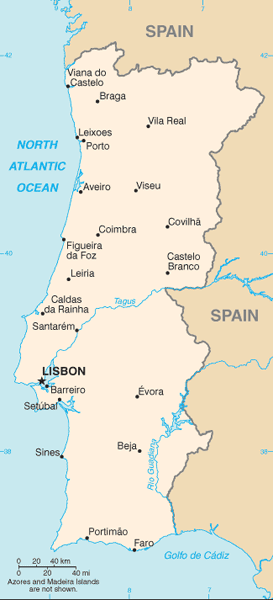
Name:Lisbon
Geographic coordinates:38 43 N, 9 08 W
Time difference:UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
Administrative divisions
18 districts (distritos, singular - distrito) and 2 autonomous regions* (regioes autonomas, singular - regiao autonoma); Aveiro, Acores (Azores)*, Beja, Braga, Braganca, Castelo Branco, Coimbra, Evora, Faro, Guarda, Leiria, Lisboa (Lisbon), Madeira*, Portalegre, Porto, Santarem, Setubal, Viana do Castelo, Vila Real, Viseu
Independence
1143 (Kingdom of Portugal recognized); 5 October 1910 (republic proclaimed)
National Holiday
Portugal Day (Dia de Portugal), 10 June (1580); note - also called Camoes Day, the day that revered national poet Luis de Camoes (1524-80) died
Constitution
adopted 2 April 1976; subsequently revised
note: the revisions placed the military under strict civilian control, trimmed the powers of the president, and laid the groundwork for a stable, pluralistic liberal democracy; they allowed for the privatization of nationalized firms and government-owned communications media
Legal system
based on civil law system; the Constitutional Tribunal reviews the constitutionality of legislation; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state:President Anibal CAVACO SILVA (since 9 March 2006)
Head of government:Prime Minister Jose SOCRATES Carvalho Pinto de Sousa (since 12 March 2005)
Cabinet:Council of Ministers appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
note: there is also a Council of State that acts as a consultative body to the president
Elections:president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 22 January 2006 (next to be held in January 2011); following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or leader of a majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the president
Election results:Anibal CAVACO SILVA elected president; percent of vote - Anibal CAVACO SILVA 50.6%, Manuel ALEGRE 20.7%, Mario Alberto Nobre Lopes SOARES 14.3%, Jeronimo DE SOUSA 8.5%, Franciso LOUCA 5.3%
Legislative branch
unicameral Assembly of the Republic or Assembleia da Republica (230 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
Elections: last held on 27 September 2009 (next to be held in fall 2013)
Election results:percent of vote by party - PS 42%, PSD 35%, CDS/PP 9%, BE 7%, CDU 7%; seats by party - PS 97, PSD 81, CDS/PP 21, BE 16, CDU 15
Judicial branch
Supreme Court (Supremo Tribunal de Justica); judges appointed for life by the Conselho Superior da Magistratura
Political Parties and Leaders
Democratic and Social Center/Popular Party or CDS/PP [Paulo PORTAS]; Portuguese Socialist Party or PS [Jose SOCRATES Carvalho Pinto de Sousa]; Social Democratic Party or PSD [Manuela FERREIRA LEITE]; The Left Bloc or BE [Franciso Anacleto LOUCA]; Unitarian Democratic Coalition or CDU [Jeronimo DE SOUSA] (includes Portuguese Communist Party or PCP and Ecologist Party ("The Greens") or PEV)
Political pressure groups and leaders
the media; labor unions
International organization participation
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE, CERN, CPLP, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, LAIA (observer), MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club (associate), PCA, Schengen Convention, SECI (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, Union Latina, UNMIT, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Joao DE VALLERA
Chancery:2012 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
Telephone:[1] (202) 328-8610
FAX:[1] (202) 462-3726
Consulate(s) general:Boston, New York, Newark (New Jersey), San Francisco
consulate(s): New Bedford (Massachusetts), Providence (Rhode Island)
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador-designate Allan J. KATZ
Embassy:Avenida das Forcas Armadas, 1600-081 Lisbon
Mailing address:Apartado 43033, 1601-301 Lisboa; PSC 83, APO AE 09726
Telephone:[351] (21) 727-3300
FAX:[351] (21) 726-9109
consulate(s): Ponta Delgada (Azores)
Flag description
two vertical bands of green (hoist side, two-fifths) and red (three-fifths) with the national coat of arms (armillary sphere and Portuguese shield) centered on the dividing line; explanations for the color meanings are ambiguous, but a popular interpretation has green symbolizing hope and red the blood of those defending the nation