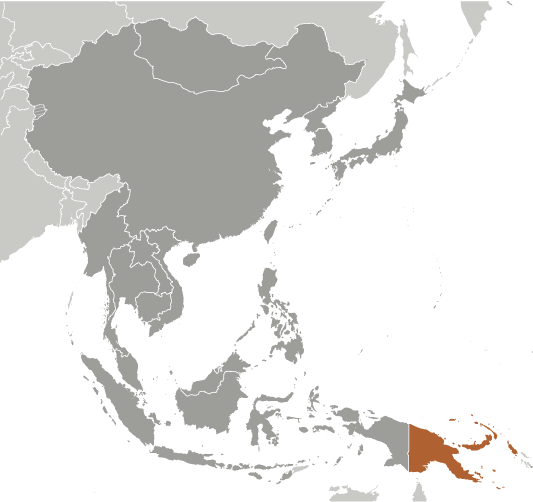
The eastern half of the island of New Guinea - second largest in the world - was divided between Germany (north) and the UK (south) in 1885. The latter area was transferred to Australia in 1902, which occupied the northern portion during World War I and continued to administer the combined areas until independence in 1975. A nine-year secessionist revolt on the island of Bougainville ended in 1997 after claiming some 20,000 lives.
Population
6,064,515 (July 2010 est.)
Country comparison to the world:105
Nationality
Noun:Papua New Guinean(s)
Adjective:Papua New Guinean
Ethnic groups
Melanesian, Papuan, Negrito, Micronesian, Polynesian
Religions
Roman Catholic 27%, Evangelical Lutheran 19.5%, United Church 11.5%, Seventh-Day Adventist 10%, Pentecostal 8.6%, Evangelical Alliance 5.2%, Anglican 3.2%, Baptist 2.5%, other Protestant 8.9%, Bahai 0.3%, indigenous beliefs and other 3.3% (2000 census)
Languages
Tok Pisin, English, and Hiri Motu are official languages; some 860 indigenous languages spoken (over one-tenth of the world's total)
note: Tok Pisin, a creole language, is widely used and understood; English is spoken by 1%-2%; Hiri Motu is spoken by less than 2%
Country Name
Conventional long form:Independent State of Papua New Guinea
Conventional short form:Papua New Guinea
Local short form:Papuaniugin
Former:Territory of Papua and New Guinea
abbreviation: PNG
Government Type
constitutional parliamentary democracy and a Commonwealth realm
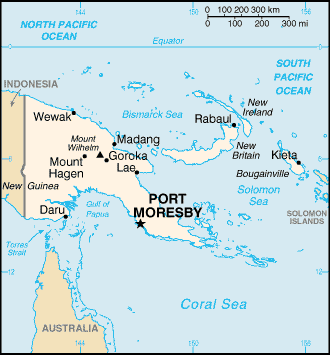
Capital
Name:Port Moresby
Geographic coordinates:9 30 S, 147 10 E
Time difference:UTC+10 (15 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
Administrative divisions
18 provinces, 1 autonomous region*, and 1 district**; Bougainville*, Central, Chimbu, Eastern Highlands, East New Britain, East Sepik, Enga, Gulf, Madang, Manus, Milne Bay, Morobe, National Capital**, New Ireland, Northern, Sandaun, Southern Highlands, Western, Western Highlands, West New Britain
Independence
16 September 1975 (from the Australian-administered UN trusteeship)
National Holiday
Independence Day, 16 September (1975)
Constitution
16 September 1975
Legal system
based on English common law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state:Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by governor general Sir Paulias MATANE (since 29 June 2004)
Head of government:Prime Minister Sir Michael SOMARE (since 2 August 2002); Deputy Prime Minister Puka TEMU (since 29 August 2007)
Cabinet:National Executive Council appointed by the governor general on the recommendation of the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:the monarchy is hereditary; the governor general nominated by parliament and appointed by the chief of state; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or leader of the majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the governor general acting in accordance with a decision of the parliament
Legislative branch
unicameral National Parliament (109 seats, 89 filled from open electorates and 20 from provinces and national capital district; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms); constitution allows up to 126 seats
Elections:last held from 30 June to 10 July 2007; next to be held in June 2012
Election results:percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA 27, PNGP 8, PAP 6, URP 6, PANGU PATI 5, PDM 5, independents 19, others 33; note - election to 1 seat was nullified
note: 15 other parties won 4 or fewer seats; association with political parties is fluid
Judicial branch
Supreme Court (the chief justice is appointed by the governor general on the proposal of the National Executive Council after consultation with the minister responsible for justice; other judges are appointed by the Judicial and Legal Services Commission)
Political Parties and Leaders
National Alliance Party or NA [Michael SOMARE]; Papua and Niugini Union Party or PANGU PATI [Andrew KUMBAKOR]; Papua New Guinea Party or PNGP [Sir Mekere MORAUTA]; People's Action Party or PAP [Gabriel KAPRIS]; People's Democratic Movement or PDM [Michael OGIO]; United Resources Party or URP [William DUMA]
Political pressure groups and leaders
Ahora [Andrew MAMOKO] (represents local tribes); Centre for Environment Law and Community Rights or Celcor [Damien ASE]; Community Coalition Against Corruption
International organization participation
ACP, ADB, AOSIS, APEC, ARF, ASEAN (observer), C, CP, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Evan Jeremy PAKI
Chancery:1779 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Suite 805, Washington, DC 20036
Telephone:[1] (202) 745-3680
FAX:[1] (202) 745-3679
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Teddy B. TAYLOR
Embassy:Douglas Street, Port Moresby, N.C.D.
Mailing address:4240 Port Moresby PI, US Department of State, Washington DC 20521-4240
Telephone:[675] 321-1455
FAX:[675] 321-3423
Flag description
divided diagonally from upper hoist-side corner; the upper triangle is red with a soaring yellow bird of paradise centered; the lower triangle is black with five, white, five-pointed stars of the Southern Cross constellation centered