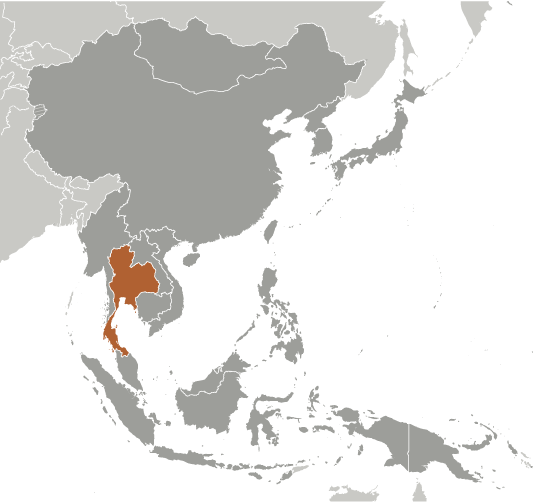
A unified Thai kingdom was established in the mid-14th century. Known as Siam until 1939, Thailand is the only Southeast Asian country never to have been taken over by a European power. A bloodless revolution in 1932 led to a constitutional monarchy. In alliance with Japan during World War II, Thailand became a US treaty ally following the conflict. A military coup in September 2006 ousted then Prime Minister THAKSIN Chinnawat. The interim government held elections in December 2007 that saw the former pro-THAKSIN People's Power Party (PPP) emerge at the head of a coalition government. The anti-THAKSIN People's Alliance for Democracy (PAD) in May 2008 began street demonstrations against the new government, eventually occupying the prime minister's office in August and Bangkok's two international airports in November. The PAD ended their protests in early December 2008 following a court ruling that dissolved the ruling PPP and two other coalition parties for election violations. The Democrat Party then formed a new coalition government and ABHISIT Wetchachiwa became prime minister. In October 2008 THAKSIN went into voluntary exile to avoid imprisonment for a corruption conviction, and has since agitated his followers from abroad. THAKSIN supporters re-organized into the United Front for Democracy Against Dictatorship (UDD) and rioted in April 2009, shutting down an ASEAN meeting in Phuket, and in early 2010 protested a court verdict confiscating most of THAKSIN's wealth. Since January 2004, thousands have been killed as separatists in Thailand's southern ethnic Malay-Muslim provinces increased the violence associated with their cause.
Country Name
Conventional long form: Kingdom of Thailand
Conventional short form:Thailand
Local long form:Ratcha Anachak Thai
Local short form:Prathet Thai
Former:Siam
Government Type
constitutional monarchy
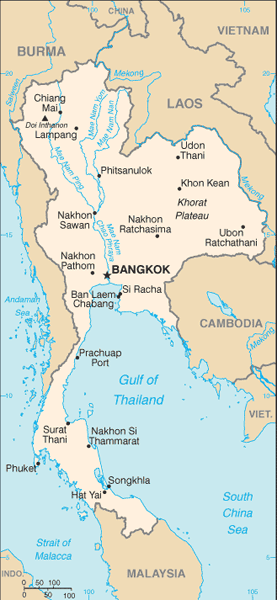
Capital
Name:Bangkok
Geographic coordinates:13 45 N, 100 31 E
Time difference:UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
Administrative divisions
76 provinces (changwat, singular and plural); Amnat Charoen, Ang Thong, Buriram, Chachoengsao, Chai Nat, Chaiyaphum, Chanthaburi, Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Chon Buri, Chumphon, Kalasin, Kamphaeng Phet, Kanchanaburi, Khon Kaen, Krabi, Krung Thep Mahanakhon (Bangkok), Lampang, Lamphun, Loei, Lop Buri, Mae Hong Son, Maha Sarakham, Mukdahan, Nakhon Nayok, Nakhon Pathom, Nakhon Phanom, Nakhon Ratchasima, Nakhon Sawan, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Nan, Narathiwat, Nong Bua Lamphu, Nong Khai, Nonthaburi, Pathum Thani, Pattani, Phangnga, Phatthalung, Phayao, Phetchabun, Phetchaburi, Phichit, Phitsanulok, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya, Phrae, Phuket, Prachin Buri, Prachuap Khiri Khan, Ranong, Ratchaburi, Rayong, Roi Et, Sa Kaeo, Sakon Nakhon, Samut Prakan, Samut Sakhon, Samut Songkhram, Sara Buri, Satun, Sing Buri, Sisaket, Songkhla, Sukhothai, Suphan Buri, Surat Thani, Surin, Tak, Trang, Trat, Ubon Ratchathani, Udon Thani, Uthai Thani, Uttaradit, Yala, Yasothon
Independence
1238 (traditional founding date; never colonized)
National Holiday
Birthday of King PHUMIPHON (BHUMIBOL), 5 December (1927)
Constitution
24 August 2007
Legal system
based on civil law system with influences of common law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
Executive branch
Chief of state:King PHUMIPHON Adunyadet, also spelled BHUMIBOL Adulyadej (since 9 June 1946)
Head of government:Prime Minister ABHISIT Wetchachiwa, also spelled ABHISIT Vejjajiva (since 17 December 2008); Deputy Prime Minister SANAN Kachornprasat, also spelled SANAN Kachornparsart (since 7 February 2008); Deputy Prime Minister SUTHEP Thueaksuban, also spelled SUTHEP Thaugsuban (since 22 December 2008); Deputy Prime Minister TRAIRONG Suwannakhiri (since 18 January 2010)
Cabinet:Council of Ministers
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
note: there is also a Privy Council advising the king
Elections:the monarchy is hereditary; according to 2007 constitution, the prime minister elected from among members of House of Representatives; following national elections for House of Representatives, the leader of the party positioned to organize a majority coalition usually becomes prime minister by appointment by the king; the prime minister limited to two four-year terms
Legislative branch
bicameral National Assembly or Rathasapha consisted of the Senate or Wuthisapha (150 seats; 76 members elected by popular vote representing 76 provinces, 74 appointed by judges and independent government bodies; members serve six-year terms) and the House of Representatives or Sapha Phuthaen Ratsadon (480 seats; 400 members elected from 157 multi-seat constituencies and 80 elected on proportional party-list basis of 10 per eight zones or groupings of provinces; members serve four-year terms)
Elections:Senate - last held on 2 March 2008 (next to be held in March 2014); House of Representatives - last election held on 23 December 2007 (next to be held by December 2011)
Election results:Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PPP 233, DP 164, TNP 34, Motherland 24, Middle Way 11, Unity 9, Royalist People's 5; following the PPP's dissolution in December 2008, most of the party's seats were assumed by its successor, the Phuea Thai Party
note: 74 senators were appointed on 19 February 2008 by a seven-member committee headed by the chief of the Constitutional Court; 76 senators were elected on 2 March 2008; elections to the Senate are non-partisan; registered political party members are disqualified from being senators
Judicial branch
Constitutional Court, Supreme Court of Justice, and Supreme Administrative Court; all judges are appointed by the king; the king's appointments to the Constitutional Courtare made upon the advice of the Senate; the nine Constitutional Court judges are drawn from the Supreme Court of Justice and Supreme Administrative Court as well as from among substantive experts in law and social sciences outside the judiciary
Political Parties and Leaders
Chat Thai Phattana Party or CP (Thai Nation Development Party) [CHUMPON Silpa-archa]; Democrat Party or DP (Prachathipat Party) [ABHISIT Wetchachiwa, also spelled ABHISIT Vejjajiva]; Motherland Party (Phuea Phaendin Party) [CHANCHAI Chairungrueng]; Phuea Thai Party (For Thais Party) or PTP [CHAWALIT Yongchaiyut]; Phumchai (Bhumjai) Thai Party or PCT (Thai Pride) [CHAWARAT Chanvirakun]; Royalist People's Party (Pracharaj) [SANOH Thienthong]; Ruam Jai Thai Party (Thai Unity Party) [WANNARAT Channukun]
Political pressure groups and leaders
People's Alliance for Democracy or PAD; United Front for Democracy Against Dictatorship or UDD
International organization participation
ADB, APEC, APT, ARF, ASEAN, BIMSTEC, BIS, CICA, CP, EAS, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OAS (observer), OIC (observer), OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE (partner), PCA, PIF (partner), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador DON Pramudwinai
Chancery:1024 Wisconsin Avenue NW, Suite 401, Washington, DC 20007
Telephone:[1] (202) 944-3600
FAX:[1] (202) 944-3611
Consulate(s) general:Chicago, Los Angeles, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Eric G. JOHN
Embassy:120-122 Wireless Road, Bangkok 10330
Mailing address: APO AP 96546
Telephone:[66] (2) 205-4000
FAX:[66] (2) 254-2990, 205-4131
consulate(s) general: Chiang Mai
Flag description
five horizontal bands of red (top), white, blue (double width), white, and red