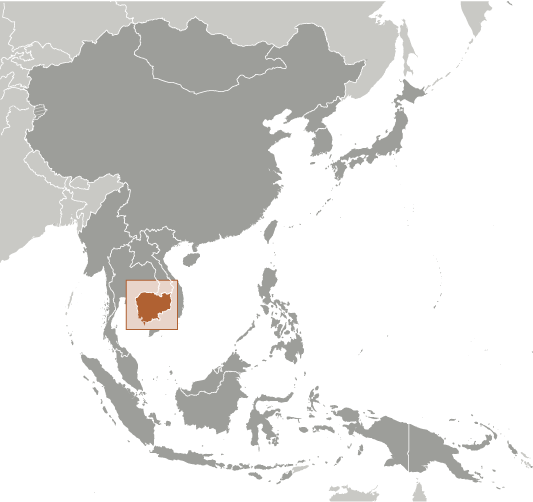
Most Cambodians consider themselves to be Khmers, descendants of the Angkor Empire that extended over much of Southeast Asia and reached its zenith between the 10th and 13th centuries. Attacks by the Thai and Cham (from present-day Vietnam) weakened the empire, ushering in a long period of decline. The king placed the country under French protection in 1863 and it became part of French Indochina in 1887. Following Japanese occupation in World War II, Cambodia gained full independence from France in 1953. In April 1975, after a five-year struggle, Communist Khmer Rouge forces captured Phnom Penh and evacuated all cities and towns. At least 1.5 million Cambodians died from execution, forced hardships, or starvation during the Khmer Rouge regime under POL POT. A December 1978 Vietnamese invasion drove the Khmer Rouge into the countryside, began a 10-year Vietnamese occupation, and touched off almost 13 years of civil war. The 1991 Paris Peace Accords mandated democratic elections and a ceasefire, which was not fully respected by the Khmer Rouge. UN-sponsored elections in 1993 helped restore some semblance of normalcy under a coalition government. Factional fighting in 1997 ended the first coalition government, but a second round of national elections in 1998 led to the formation of another coalition government and renewed political stability. The remaining elements of the Khmer Rouge surrendered in early 1999. Some of the surviving Khmer Rouge leaders are awaiting trial for crimes against humanity by a hybrid UN-Cambodian tribunal supported by international assistance. Elections in July 2003 were relatively peaceful, but it took one year of negotiations between contending political parties before a coalition government was formed. In October 2004, King Norodom SIHANOUK abdicated the throne and his son, Prince Norodom SIHAMONI, was selected to succeed him. Local elections were held in Cambodia in April 2007, with little of the pre-election violence that preceded prior elections. National elections in July 2008 were relatively peaceful.
Country Name
Conventional long form:Kingdom of Cambodia
Conventional short form:Cambodia
Local long form:Preahreacheanachakr Kampuchea (phonetic pronunciation)
Local short form:Kampuchea
Former: Khmer Republic, Democratic Kampuchea, People's Republic of Kampuchea, State of Cambodia
Government Type
multiparty democracy under a constitutional monarchy
Capital
Name: Phnom Penh
Geographic coordinates:11 33 N, 104 55 E
Time difference: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
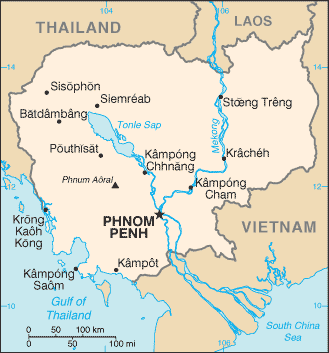
Administrative divisions
23 provinces (khett, singular and plural) and 1 municipality (krong, singular and plural)
provinces: Banteay Mean Cheay, Batdambang, Kampong Cham, Kampong Chhnang, Kampong Spoe, Kampong Thum, Kampot, Kandal, Kaoh Kong, Keb, Krachen, Mondol Kiri, Otdar Mean Cheay, Pailin, Pouthisat, Preah Seihanu (Sihanoukville), Preah Vihear, Prey Veng, Rotanah Kiri, Siem Reab, Stoeng Treng, Svay Rieng, Takev
municipalities: Phnum Penh (Phnom Penh)
Independence
9 November 1953 (from France)
National Holiday
Independence Day, 9 November (1953)
Constitution
promulgated 21 September 1993
Legal system
primarily a civil law mixture of French-influenced codes from the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) period, royal decrees, and acts of the legislature with influences of customary law and remnants of communist legal theory; increasing influence of common law; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state: King Norodom SIHAMONI (since 29 October 2004)
Head of government:Prime Minister HUN SEN (since 14 January 1985) [co-prime minister from 1993 to 1997]; Permanent Deputy Prime Minister MEN SAM AN (since 25 September 2008); Deputy Prime Ministers SAR KHENG (since 3 February 1992); SOK AN, TEA BANH, HOR NAMHONG, NHEK BUNCHHAY (since 16 July 2004); BIN CHHIN (since 5 September 2007); KEAT CHHON, YIM CHHAI LY (since 24 September 2008); KE KIMYAN (since 12 March 2009)
Cabinet:Council of Ministers named by the prime minister and appointed by the monarch
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:the king chosen by a Royal Throne Council from among all eligible males of royal descent; following legislative elections, a member of the majority party or majority coalition named prime minister by the Chairman of the National Assembly and appointed by the king
Legislative branch
bicameral, consists of the Senate (61 seats; 2 members appointed by the monarch, 2 elected by the National Assembly, and 57 elected by parliamentarians and commune councils; members serve five-year terms) and the National Assembly (123 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
Elections:Senate - last held on 22 January 2006 (next to be held in January 2011); National Assembly - last held on 27 July 2008 (next to be held in July 2013)
Election results:Senate - percent of vote by party - CPP 69%, FUNCINPEC 21%, SRP 10%; seats by party - CPP 45, FUNCINPEC 10, SRP 2; National Assembly - percent of vote by party - CPP 58%, SRP 22%, HRP 7%; NRP 6%; FUNCINPEC 5%; others 2%; seats by party - CPP 90, SRP 26, HRP 3, FUNCINPEC 2, NRP 2
Judicial branch
Supreme Council of the Magistracy (provided for in the constitution and formed in December 1997); Supreme Court (and lower courts) exercises judicial authority
Political Parties and Leaders
Cambodian People's Party or CPP [CHEA SIM]; Human Rights Party or HRP [KHEM SOKHA, also spelled KEM SOKHA]; National United Front for an Independent, Neutral, Peaceful, and Cooperative Cambodia or FUNCINPEC [KEV PUT REAKSMEI]; Nationalist Party or NP [CHHIM SEAK LENG] (formerly the NRP); Sam Rangsi Party or SRP [SAM RANGSI, also spelled SAM RAINSY]
Political pressure groups and leaders
Cambodian Freedom Fighters or CFF; Partnership for Transparency Fund or PTF (anti-corruption organization); Students Movement for Democracy; The Committee for Free and Fair Elections or Comfrel
Other:human rights organizations; vendors
International organization participation
ACCT, ADB, APT, ARF, ASEAN, EAS, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (subscriber), ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMIS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador HENG HEM
Chancery: 4530 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20011
Telephone: [1] (202) 726-7742
FAX:[1] (202) 726-8381
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Carol A. RODLEY
Embassy:#1, Street 96, Sangkat Wat Phnom, Khan Daun Penh, Phnom Penh
Mailing address:Box P, APO AP 96546
Telephone: [855] (23) 728-000
FAX:[855] (23) 728-600
Flag description
three horizontal bands of blue (top), red (double width), and blue with a white three-towered temple representing Angkor Wat outlined in black in the center of the red band; red and blue are traditional Cambodian colors
note: only national flag to incorporate an actual building in its design