Upon independence in 1960, the former French region of Middle Congo became the Republic of the Congo. A quarter century of experimentation with Marxism was abandoned in 1990 and a democratically elected government took office in 1992. A brief civil war in 1997 restored former Marxist President Denis SASSOU-NGUESSO, and ushered in a period of ethnic and political unrest. Southern-based rebel groups agreed to a final peace accord in March 2003, but the calm is tenuous and refugees continue to present a humanitarian crisis. The Republic of Congo was once one of Africa's largest petroleum producers, but with declining production it will need new offshore oil finds to sustain its oil earnings over the long term.
Population
4,125,916
Country comparison to the world:126
note:estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2010 est.)
Nationality
Noun:Congolese (singular and plural)
Adjective:Congolese or Congo
Ethnic groups
Kongo 48%, Sangha 20%, M'Bochi 12%, Teke 17%, Europeans and other 3%
Religions
Christian 50%, animist 48%, Muslim 2%
Languages
French (official), Lingala and Monokutuba (lingua franca trade languages), many local languages and dialects (of which Kikongo is the most widespread)
Country Name
Conventional long form:Republic of the Congo
Conventional short form:Congo (Brazzaville)
Local long form:Republique du Congo
Local short form:none
Former:Middle Congo, Congo/Brazzaville, Congo
Government Type
republic
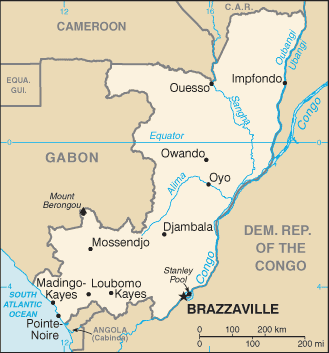
Capital
Name:Brazzaville
Geographic coordinates:4 15 S, 15 17 E
Time difference:UTC+1 (six hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
Administrative divisions
10 regions (regions, singular - region) and 1 commune*; Bouenza, Brazzaville*, Cuvette, Cuvette-Ouest, Kouilou, Lekoumou, Likouala, Niari, Plateaux, Pool, Sangha
Independence
15 August 1960 (from France)
National Holiday
Independence Day, 15 August (1960)
Constitution
approved by referendum 20 January 2002
Legal system
based on French civil law system and customary law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state:President Denis SASSOU-Nguesso (since 25 October 1997, following the civil war in which he toppled elected president Pascal LISSOUBA); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
Head of government:President Denis SASSOU-Nguesso (since 25 October 1997); note - the position of prime minister was abolished in September 2009
Cabinet:Council of Ministers appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:president elected by popular vote for a seven-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 12 July 2009 (next to be held in 2016)
Election results:Denis SASSOU-NGUESSO reelected president; percent of vote - Denis SASSOU-NGUESSO 78.6%, Joseph Kignoumbi Kia MBOUNGOU 7.5%, Nicephore Fylla de SAINT-EUDES 7%
Legislative branch
bicameral Parliament consists of the Senate (72 seats; members elected by indirect vote to serve five-year terms) and the National Assembly (137 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
Elections:Senate - last held on 5 August 2008 (next to be held in 2013); National Assembly - last held on 24 June and 5 August 2007 (next to be held in 2012)
Election results:Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - RMP 33, FDU 23, UPADS 2, independents 7, other 7; National Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PCT 46, MCDDI 11, UPADS 11, MAR 5, MSD 5, independents 37, other 22
Judicial branch
Supreme Court or Cour Supreme
Political Parties and Leaders
Action Movement for Renewal or MAR; Congolese Labour Party or PCT; Congolese Movement for Democracy and Integral Development or MCDDI [Michel MAMPOUYA]; Movement for Solidarity and Development or MSD; Pan-African Union for Social Development or UPADS [Martin MBERI]; Rally for Democracy and the Republic or RDR [Raymond Damasge NGOLLO]; Rally for Democracy and Social Progress or RDPS [Jean-Pierre Thystere TCHICAYA, president]; Rally of the Presidential Majority or RMP; Union for Democracy and Republic or UDR; United Democratic Forces or FDU [Sebastian EBAO]; many less important parties
Political pressure groups and leaders
Congolese Trade Union Congress or CSC; General Union of Congolese Pupils and Students or UGEEC; Revolutionary Union of Congolese Women or URFC; Union of Congolese Socialist Youth or UJSC
International organization participation
ACCT, ACP, AfDB, AU, BDEAC, CEMAC, FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission: Ambassador Serge MOMBOULI
Chancery: 4891 Colorado Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20011
Telephone:[1] (202) 726-5500
FAX:[1] (202) 726-1860
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Allan EASTHAM
Embassy:Boulevard de la Revolution, BDEAC Building, 4th Floor, Brazzaville; note - a new embassy is expected to open in 2009
Mailing address:B.P. 1015, Brazzaville
Telephone:[242] 281-1481, 281-3368; note - until the new embassy in Brazzaville becomes operational, some duties will still be handled in the US embassy in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Flag description
divided diagonally from the lower hoist side by a yellow band; the upper triangle (hoist side) is green and the lower triangle is red; green symbolizes agriculture and forests, yellow the friendship and nobility of the people, red is unexplained but has been associated with the struggle for independence
note: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia