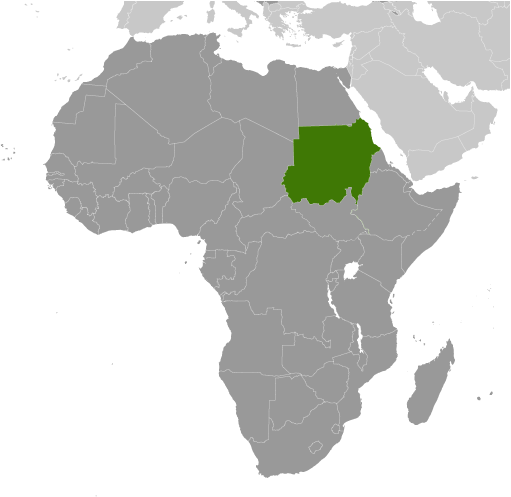
Military regimes favoring Islamic-oriented governments have dominated national politics since independence from the UK in 1956. Sudan was embroiled in two prolonged civil wars during most of the remainder of the 20th century. These conflicts were rooted in northern economic, political, and social domination of largely non-Muslim, non-Arab southern Sudanese. The first civil war ended in 1972 but broke out again in 1983. The second war and famine-related effects resulted in more than four million people displaced and, according to rebel estimates, more than two million deaths over a period of two decades. Peace talks gained momentum in 2002-04 with the signing of several accords. The final North/South Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA), signed in January 2005, granted the southern rebels autonomy for six years followed by a referendum on independence for Southern Sudan. The referendum was held in January 2011 and indicated overwhelming support for independence. South Sudan became independent on 9 July 2011. Since southern independence Sudan has been combating rebels from the Sudan People's Liberation Movement-North (SPLM-N) in Southern Kordofan and Blue Nile states. A separate conflict, which broke out in the western region of Darfur in 2003, has displaced nearly two million people and caused an estimated 200,000 to 400,000 deaths. The UN took command of the Darfur peacekeeping operation from the African Union in December 2007. Peacekeeping troops have struggled to stabilize the situation, which has become increasingly regional in scope and has brought instability to eastern Chad. Sudan also has faced large refugee influxes from neighboring countries primarily Ethiopia and Chad. Armed conflict, poor transport infrastructure, and lack of government support have chronically obstructed the provision of humanitarian assistance to affected populations.
Country Name
Conventional long form:Republic of the Sudan
Conventional short form:Sudan
Local long form:Jumhuriyat as-Sudan
Local short form:As-Sudan
Former:Anglo-Egyptian Sudan
Government Type
Federal republic ruled by the National Congress Party the (NCP), which came to power by military coup in 1989; the CPA-mandated Government of National Unity, which since 2005 provided a percentage of leadership posts to the south Sudan-based Sudan People's Liberation Movement (SPLM), was disbanded following the secession of South Sudan.
Capital
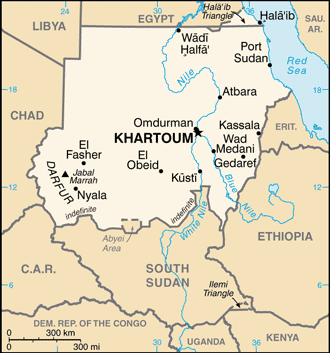
Name:Khartoum
Geographic coordinates:15 36 N, 32 32 E
Time difference:UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
Administrative divisions
15 states (wilayat, singular - wilayah); Al Bahr al Ahmar (Red Sea), Al Jazira (Gezira), Al Khartoum (Khartoum), Al Qadarif (Gedaref), An Nil al Abyad (White Nile), An Nil al Azraq (Blue Nile), Ash Shimaliyya (Northern), Gharb Darfur (Western Darfur), Janub Darfur (Southern Darfur), Janub Kurdufan (Southern Kordofan), Kassala, Nahr an Nil (River Nile), Shimal Darfur (Northern Darfur), Shimal Kurdufan (Northern Kordofan), Sinnar
note: the Sudanese Government has announced the creation of two new states, Central Darfur and East Darfur, but they are not yet operational
Independence
1 January 1956 (from Egypt and the UK)
National Holiday
Independence Day, 1 January (1956)
Constitution
The Government of Sudan is in the process of drafting a new constitution to replace the Interim National Constitution ratified 5 July 2005
Legal system
mixed legal system of Islamic law and English common law
Suffrage
17 years of age; universal
Executive branch
President Umar Hassan Ahmad al-BASHIR (since 16 October 1993); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
Head of government:President Umar Hassan Ahmad al-BASHIR (since 16 October 1993)
Cabinet:Council of Ministers appointed by the president; note - the NCP (formerly the National Islamic Front or NIF) dominates al-BASHIR's cabinet
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:election on 11-15 April 2010; next to be held in 2015
Election results: Umar Hassan Ahmad al-BASHIR reelected president; percent of vote - Umar Hassan Ahmad al-BASHIR 68.2%, Yasir ARMAN 21.7%, Abdullah Deng NHIAL 3.9%, others 6.2%
note: al-BASHIR assumed power as chairman of Sudan's Revolutionary Command Council for National Salvation (RCC) in June 1989 and served concurrently as chief of state, chairman of the RCC, prime minister, and minister of defense until mid-October 1993 when he was appointed president by the RCC; he was elected president by popular vote for the first time in March 1996
Legislative branch
bicameral National Legislature consists of a Council of States (50 seats; members indirectly elected by state legislatures to serve six-year terms) and a National Assembly (450 seats; 60% from geographic constituencies, 25% from a women's list, and 15% from party lists; members to serve six-year terms)
Elections: last held on 11-15 April 2010 (next to be held in 2016)
Election results:National Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NCP 323, SPLM 99, PCP 4, DUP 4, UFP 3, URRP 2, DUPO 2, SPLM-DC 2, other 7, vacant 4
Judicial branch
Constitutional Court of nine justices; National Supreme Court; National Courts of Appeal; other national courts; National Judicial Service Commission will undertake overall management of the National Judiciary
Political Parties and Leaders
Democratic Unionist Party or DUP [Hatim al-SIR]; Democratic Unionist Party-Original or DUPO; National Congress Party or NCP [Umar Hassan al-BASHIR]; Popular Congress Party or PCP [Hassan al-TURABI]; Umma Federal Party or UFP; Umma Renewal and Reform Party or URRP
Political pressure groups and leaders
Umma Party [SADIQ Siddiq al-Mahdi]; Popular Congress Party or PCP [Hassan al-TURABI]; Democratic Unionist Party [Muhammad Uthman al-Mirghani]; Darfur rebel groups including the Justice and Equality Movement or JEM [Khalil IBRAHIM] and the Sudan Liberation Movement or SLM [various factional leaders]
International organization participation
ABEDA, ACP, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AU, CAEU, COMESA, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Emad Mirghani ALTOHAMY
Chancery:2210 2210 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
Telephone:[1] (202) 338-8565
FAX:[1] (202) 667-2406
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Mary Carlin YATES
Embassy:Sharia Ali Abdul Latif Street, Khartoum
Mailing address:P.O. Box 699, Khartoum; APO AE 09829
Telephone:[249] (183) 774700 through 704
FAX:[249] (183) 774137
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and black with a green isosceles triangle based on the hoist side; colors and design based on the Arab Revolt flag of World War I, but the meanings of the colors are expressed as follows: red signifies the struggle for freedom, white is the color of peace, light, and love, black represents Sudan itself (in Arabic 'Sudan' means black), green is the color of Islam, agriculture, and prosperity