The UK established a protectorate over the Solomon Islands in the 1890s. Some of the most bitter fighting of World War II occurred on this archipelago. Self-government was achieved in 1976 and independence two years later. Ethnic violence, government malfeasance, and endemic crime have undermined stability and civil society. In June 2003, then Prime Minister Sir Allan KEMAKEZA sought the assistance of Australia in reestablishing law and order; the following month, an Australian-led multinational force arrived to restore peace and disarm ethnic militias. The Regional Assistance Mission to the Solomon Islands (RAMSI) has generally been effective in restoring law and order and rebuilding government institutions.
Population
609,794 (July 2010 est.)
Country comparison to the world:167
Nationality
Noun:Solomon Islander(s)
Adjective:Solomon Islander
Ethnic groups
Melanesian 94.5%, Polynesian 3%, Micronesian 1.2%, other 1.1%, unspecified 0.2% (1999 census)
Religions
Church of Melanesia 32.8%, Roman Catholic 19%, South Seas Evangelical 17%, Seventh-Day Adventist 11.2%, United Church 10.3%, Christian Fellowship Church 2.4%, other Christian 4.4%, other 2.4%, unspecified 0.3%, none 0.2% (1999 census)
Languages
Melanesian pidgin in much of the country is lingua franca; English (official but spoken by only 1%-2% of the population); 120 indigenous languages
Country Name
Conventional long form:none
Conventional short form:Solomon Islands
Local long form:none
Local short form:Solomon Islands
Former:British Solomon Islands
Government Type
parliamentary democracy and a Commonwealth realm
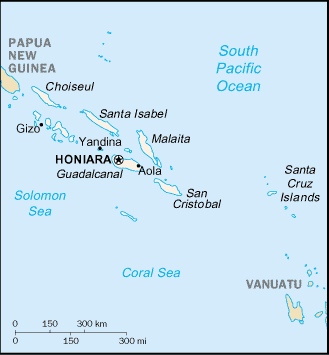
Capital
Name:Honiara
Geographic coordinates: 9 26 S, 159 57 E
Time difference:UTC+11 (16 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
Administrative divisions
9 provinces and 1 capital territory*; Central, Choiseul, Guadalcanal, Honiara*, Isabel, Makira, Malaita, Rennell and Bellona, Temotu, Western
Independence
7 July 1978 (from the UK)
National Holiday
Independence Day, 7 July (1978)
Constitution
7 July 1978
Legal system
English common law, which is widely disregarded; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
21 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state:Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor General Frank KABUI (since 7 July 2009)
Head of government:Prime Minister Derek SIKUA (since 20 December 2007); note - Prime Minister Manasseh SOGAVARE defeated in a no confidence vote in parliament on 13 December 2007; SIKUA elected on 20 December 2007
Cabinet:Cabinet consists of 20 members appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister from among the members of parliament
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch on the advice of parliament for up to five years (eligible for a second term); following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or the leader of a majority coalition usually elected prime minister by parliament; deputy prime minister appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister from among the members of parliament
Legislative branch
unicameral National Parliament (50 seats; members elected from single-member constituencies by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
Elections:last held on 5 April 2006 (next to be held in 2010)
Election results:percent of vote by party - National Party 6.9%, PAP 6.3%, SIPRA 6.3%, Liberal 5%, Democratic 4.9%, SOCRED 4.3%, LAFARI 2.8%, independents 60.3%; seats by party - National Party 4, SIPRA 4, Democratic 3, PAP 3, LAFARI 2, Liberal 2, SOCRED 2, independents 30
Judicial branch
Court of Appeal
Political Parties and Leaders
Association of Independent Members or AIM [Thomas CHAN]; Christian Alliance Solomon Islands or CASI [Edward RONIA]; LAFARI Party [John GARO]; National Party [Francis HILLY]; People's Alliance Party or PAP [Sir Allan KEMAKEZA]; Social Credit Party or SOCRED [Manasseh Damukana SOGAVARE]; Solomon First Party [David QUAN]; Solomon Islands Democratic Party [Gabriel SURI]; Solomon Islands Labor Party or SILP [Joses TUHANUKU]; Solomon Islands Liberal Party [Bartholomew ULUFA'ALU]; Solomon Islands Party for Rural Advancement or SIPRA [Job D. TAUSINGA]; United Party [Sir Peter KENILOREA]
note: in general, Solomon Islands politics is characterized by fluid coalitions
Political pressure groups and leaders
Isatabu Freedom Movement (IFM); Malaita Eagle Force (MEF); note - these rival armed ethnic factions crippled the Solomon Islands in a wave of violence from 1999 to 2003
International organization participation
ACP, ADB, AOSIS, C, ESCAP, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IOC, ITU, MIGA, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WHO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Collin David BECK
Chancery:800 Second Avenue, Suite 400L, New York, NY 10017
Telephone:[1] (212) 599-6192, 6193
FAX:[1] (212) 661-8925
Diplomatic representation from the US
the US does not have an embassy in Solomon Islands (embassy closed July 1993); the ambassador to Papua New Guinea is accredited to the Solomon Islands
Flag description
divided diagonally by a thin yellow stripe from the lower hoist-side corner; the upper triangle (hoist side) is blue with five white five-pointed stars arranged in an X pattern; the lower triangle is green