Aboriginal settlers arrived on the continent from Southeast Asia about 40,000 years before the first Europeans began exploration in the 17th century. No formal territorial claims were made until 1770, when Capt. James COOK took possession in the name of Great Britain. Six colonies were created in the late 18th and 19th centuries; they federated and became the Commonwealth of Australia in 1901. The new country took advantage of its natural resources to rapidly develop agricultural and manufacturing industries and to make a major contribution to the British effort in World Wars I and II. In recent decades, Australia has transformed itself into an internationally competitive, advanced market economy. It boasted one of the OECD's fastest growing economies during the 1990s, a performance due in large part to economic reforms adopted in the 1980s. Long-term concerns include climate-change issues such as the depletion of the ozone layer and more frequent droughts, and management and conservation of coastal areas, especially the Great Barrier Reef.
Country Name
Conventional long form: Commonwealth of Australia
Conventional short form: Australia
Government Type
federal parliamentary democracy and a Commonwealth realm
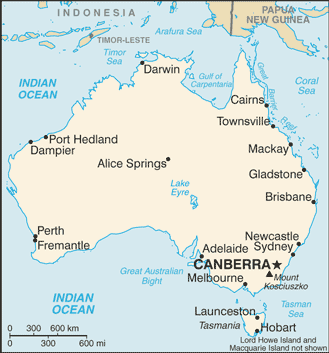
Capital
Name: Canberra
Geographic coordinates: 35 17 S, 149 13 E
Time difference: UTC+10 (15 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins first Sunday in October; ends first Sunday in April
note: Australia is divided into three time zones
Administrative divisions
6 states and 2 territories*; Australian Capital Territory*, New South Wales, Northern Territory*, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, Western Australia
Independence
1 January 1901 (from the federation of UK colonies)
National Holiday
Australia Day, 26 January (1788); ANZAC Day (commemorated as the anniversary of the landing of troops of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps during World War I at Gallipoli, Turkey), 25 April (1915)
Constitution
9 July 1900; effective on 1 January 1901
Legal system
based on English common law; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
Executive branch
Chief of state: Queen of Australia ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor General Quentin BRYCE (since 5 September 2008)
Head of government: Prime Minister Kevin RUDD (since 3 December 2007); Deputy Prime Minister Julia GILLARD (since 3 December 2007)
Cabinet: prime minister nominates, from among members of Parliament, candidates who are subsequently sworn in by the governor general to serve as government ministers
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch on the recommendation of the prime minister; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or leader of a majority coalition is sworn in as prime minister by the governor general
Legislative branch
the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch on the recommendation of the prime minister; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or leader of a majority coalition is sworn in as prime minister by the governor general
Elections: Senate - last held on 24 November 2007 (next to be held no later than 2010); House of Representatives - last held on 24 November 2007 (next to be called no later than 2010)
Election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Liberal Party-National Party coalition 37, Australian Labor Party 32, Australian Greens 5, Family First Party 1, independent 1; House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Australian Labor Party 83, Liberal Party 55, National Party 10, independents 2
Judicial branch
High Court (the chief justice and six other justices are appointed by the governor general)
Political Parties and Leaders
Australian Democrats [Julia MELLAND]; Australian Greens [Bob BROWN]; Australian Labor Party [Kevin RUDD]; Country Liberal Party [Terry MILLS]; Family First Party [Steve FIELDING]; Liberal Party [Tony ABBOTT]; The Nationals [Warren TRUSS]
Political pressure groups and leaders
Other: business groups; environmental groups; social groups; trade unions
International organization participation
ADB, ANZUS, APEC, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, C, CP, EAS, EBRD, FAO, FATF, G-20, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NEA, NSG, OECD, OPCW, Paris Club, PCA, PIF, SAARC (observer), Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNMIS, UNMIT, UNRWA, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission: Ambassador Kim Christian BEAZLEY
Chancery: 1601 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
Telephone: [1] (202) 797-3000
FAX: [1] (202) 797-3168
Consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Chicago, Honolulu, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission: Ambassador Jeffrey L. BLEICH
Embassy: Moonah Place, Yarralumla, Canberra, Australian Capital Territory 2600
Mailing address:APO AP 96549
Telephone: [61] (02) 6214-5600
FAX: [61] (02) 6214-5970
consulate(s) general: Melbourne, Perth, Sydney
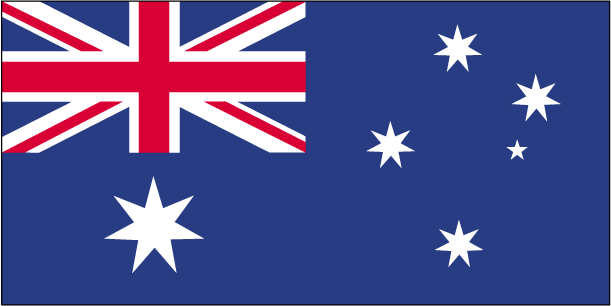
Flag description
blue with the flag of the UK in the upper hoist-side quadrant and a large seven-pointed star in the lower hoist-side quadrant known as the Commonwealth or Federation Star, representing the federation of the colonies of Australia in 1901; the star depicts one point for each of the six original states and one representing all of Australia's internal and external territories; on the fly half is a representation of the Southern Cross constellation in white with one small five-pointed star and four larger, seven-pointed stars