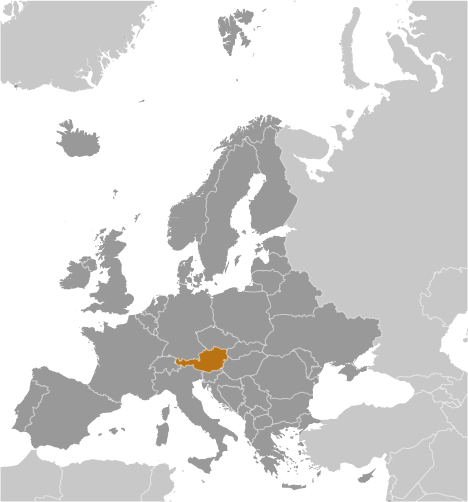
Once the center of power for the large Austro-Hungarian Empire, Austria was reduced to a small republic after its defeat in World War I. Following annexation by Nazi Germany in 1938 and subsequent occupation by the victorious Allies in 1945, Austria's status remained unclear for a decade. A State Treaty signed in 1955 ended the occupation, recognized Austria's independence, and forbade unification with Germany. A constitutional law that same year declared the country's "perpetual neutrality" as a condition for Soviet military withdrawal. The Soviet Union's collapse in 1991 and Austria's entry into the European Union in 1995 have altered the meaning of this neutrality. A prosperous, democratic country, Austria entered the EU Economic and Monetary Union in 1999. In January 2009, Austria assumed a nonpermanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2009-10 term.
Population
8,214,160 (July 2010 est.)
Country comparison to the world: 92
Nationality
Noun:Austrian(s))
Adjective:Austrian
Ethnic groups
Austrians 91.1%, former Yugoslavs 4% (includes Croatians, Slovenes, Serbs, and Bosniaks), Turks 1.6%, German 0.9%, other or unspecified 2.4% (2001 census)
Religions
Roman Catholic 73.6%, Protestant 4.7%, Muslim 4.2%, other 3.5%, unspecified 2%, none 12% (2001 census)
Languages
German (official nationwide) 88.6%, Turkish 2.3%, Serbian 2.2%, Croatian (official in Burgenland) 1.6%, other (includes Slovene, official in Carinthia, and Hungarian, official in Burgenland) 5.3% (2001 census)
Country Name
Conventional long form: Republic of Austria
Conventional short form: Austria
Local long form: Republik Oesterreich
Local short form: Oesterreich
Government Type
federal republic
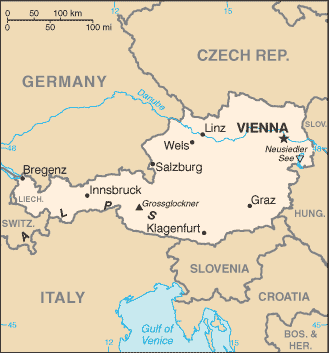
Capital
Name: Vienna
Geographic coordinates: 48 12 N, 16 22 E
Time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
Administrative divisions
9 states (Bundeslaender, singular - Bundesland); Burgenland, Kaernten (Carinthia), Niederoesterreich (Lower Austria), Oberoesterreich (Upper Austria), Salzburg, Steiermark (Styria), Tirol (Tyrol), Vorarlberg, Wien (Vienna)
Independence
976 (Margravate of Austria established); 17 September 1156 (Duchy of Austria founded); 11 August 1804 (Austrian Empire proclaimed); 12 November 1918 (republic proclaimed)
National Holiday
National Day, 26 October (1955); note - commemorates the passage of the law on permanent neutrality
Constitution
1920; revised 1929; reinstated 1 May 1945; note - during the period 1 May 1934-1 May 1945 there was a fascist (corporative) constitution in place
Legal system
civil law system with Roman law origin; judicial review of legislative acts by the Constitutional Court; separate administrative and civil/penal supreme courts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
16 years of age; universal; note - reduced from 18 years of age in 2007
Executive branch
Chief of state: President Heinz FISCHER (SPOe) (since 8 July 2004)
Head of government: Chancellor Werner FAYMANN (SPOe) (since 2 December 2008); Vice Chancellor Josef PROELL (OeVP) (since 2 December 2008)
Cabinet: Council of Ministers chosen by the president on the advice of the chancellor
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections: president elected by direct popular vote for a six-year term (eligible for a second term); presidential election last held on 25 April 2010 (next to be held on 25 April 2016); chancellor formally chosen by the president but determined by the coalition parties forming a parliamentary majority; vice chancellor chosen by the president on the advice of the chancellor
Election results: Heinz FISCHER reelected president; percent of vote - Heinz FISCHER 79.3%, Barbara ROSENKRANZ 15.2%, Rudolf GEHRING 5.4%
note: government coalition - SPOe and OeVP
Legislative branch
bicameral Federal Assembly or Bundesversammlung consists of Federal Council or Bundesrat (62 seats; members chosen by state parliaments with each state receiving 3 to 12 members in proportion to its population; members serve five- or six-year terms) and the National Council or Nationalrat (183 seats; members elected by direct popular vote to serve five-year terms)
note: on rare occasions the government may convene a Loya Jirga (Grand Council) on issues of independence, national sovereignty, and territorial integrity; it can amend the provisions of the constitution and prosecute the president; it is made up of members of the National Assembly and chairpersons of the provincial and district councils
Elections: National Council - last held on 28 September 2008 (next to be held by September 2013)
Election results: National Council - percent of vote by party - SPOe 29.3%, OeVP 26%, FPOe 17.5%, BZOe 10.7%, Greens 10.4%, other 6.1%; seats by party - SPOe 57, OeVP 51, FPOe 34, BZOe 21, Greens 20
Judicial branch
Supreme Judicial Court or Oberster Gerichtshof; Administrative Court or Verwaltungsgerichtshof; Constitutional Court or Verfassungsgerichtshof
Political Parties and Leaders
Alliance for the Future of Austria or BZOe [Josef BUCHER]; Austrian People's Party or OeVP [Josef PROELL]; Freedom Party of Austria or FPOe [Heinz Christian STRACHE]; Social Democratic Party of Austria or SPOe [Werner FAYMANN]; The Greens [Eva GLAWISCHNIG]
Political pressure groups and leaders
Austrian Trade Union Federation or OeGB (nominally independent but primarily Social Democratic); Federal Economic Chamber; OeVP-oriented Association of Austrian Industrialists or IV; Roman Catholic Church, including its chief lay organization, Catholic Action
Other: Three composite leagues of the Austrian People's Party or OeVP representing business, labor, farmers, and other nongovernment organizations in the areas of environment and human rights
International organization participation
ACCT (observer), ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-9, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MINURCAT, MINURSO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PFP, Schengen Convention, SECI (observer), UN, UN Security Council (temporary), UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Christian PROSL
Chancery: 3524 International Court NW, Washington, DC 20008-3035
Telephone: [1] (202) 895-6700
FAX: [[1] (202) 895-6750
Consulate(s) general: Chicago, Los Angeles, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission: Ambassador William C. EACHO III
Embassy:Boltzmanngasse 16, A-1090, Vienna
Mailing address: use embassy street address
Telephone: [43] (1) 31339-0
FAX: [43] (1) 3100682
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and red; the flag design is certainly one of the oldest - if not the oldest - national banners in the world; according to tradition, in 1191, following a fierce battle in the Third Crusade, Duke Leopold V of Austria's white tunic became completely blood-spattered; upon removal of his wide belt or sash, a white band was revealed; the red-white-red color combination was subsequently adopted as his banner
note: Afghanistan had more changes to its national flag in the 20th century than any other country; the colors black, red, and green appeared on most of them