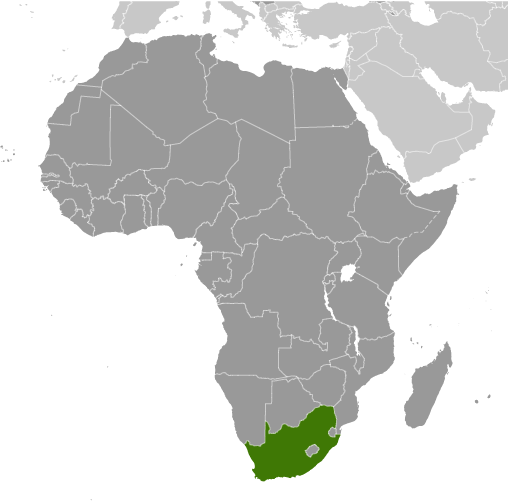
Dutch traders landed at the southern tip of modern day South Africa in 1652 and established a stopover point on the spice route between the Netherlands and the Far East, founding the city of Cape Town. After the British seized the Cape of Good Hope area in 1806, many of the Dutch settlers (the Boers) trekked north to found their own republics. The discovery of diamonds (1867) and gold (1886) spurred wealth and immigration and intensified the subjugation of the native inhabitants. The Boers resisted British encroachments but were defeated in the Boer War (1899-1902); however, the British and the Afrikaners, as the Boers became known, ruled together beginning in 1910 under the Union of South Africa, which became a republic in 1961 after a whites-only referendum. In 1948, the National Party was voted into power and instituted a policy of apartheid - the separate development of the races - which favored the white minority at the expense of the black majority. The African National Congress (ANC) led the opposition to apartheid and many top ANC leaders, such as Nelson MANDELA, spent decades in South Africa's prisons. Internal protests and insurgency, as well as boycotts by some Western nations and institutions, led to the regime's eventual willingness to negotiate a peaceful transition to majority rule. The first multi-racial elections in 1994 brought an end to apartheid and ushered in majority rule under an ANC-led government. South Africa since then has struggled to address apartheid-era imbalances in decent housing, education, and health care. ANC infighting, which has grown in recent years, came to a head in September 2008 when President Thabo MBEKI resigned, and Kgalema MOTLANTHE, the party's General-Secretary, succeeded him as interim president. Jacob ZUMA became president after the ANC won general elections in April 2009.
Population
49,109,107
Country comparison to the world:25
note:estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2010 est.)
Nationality
Noun:South African(s)
Adjective:South African
Ethnic groups
black African 79%, white 9.6%, colored 8.9%, Indian/Asian 2.5% (2001 census)
Religions
Zion Christian 11.1%, Pentecostal/Charismatic 8.2%, Catholic 7.1%, Methodist 6.8%, Dutch Reformed 6.7%, Anglican 3.8%, Muslim 1.5%, other Christian 36%, other 2.3%, unspecified 1.4%, none 15.1% (2001 census)
Languages
IsiZulu 23.8%, IsiXhosa 17.6%, Afrikaans 13.3%, Sepedi 9.4%, English 8.2%, Setswana 8.2%, Sesotho 7.9%, Xitsonga 4.4%, other 7.2% (2001 census)
Country Name
Conventional long form:Republic of South Africa
Conventional short form:South Africa
Former:Union of South Africa
abbreviation: RSA
Government Type
republic
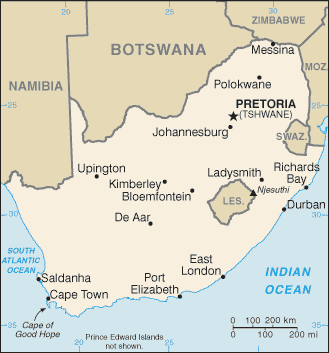
Capital
Name:Pretoria (administrative capital)
Geographic coordinates:25 42 S, 28 13 E
Time difference:UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
note: Cape Town (legislative capital); Bloemfontein (judicial capital)
Administrative divisions
9 provinces; Eastern Cape, Free State, Gauteng, KwaZulu-Natal, Limpopo, Mpumalanga, Northern Cape, North-West, Western Cape
Independence
31 May 1910 (Union of South Africa formed from four British colonies: Cape Colony, Natal, Transvaal, and Orange Free State); 31 May 1961 (republic declared) 27 April 1994 (majority rule)
National Holiday
Freedom Day, 27 April (1994)
Constitution
10 December 1996; note - certified by the Constitutional Court on 4 December 1996; was signed by then President MANDELA on 10 December 1996; and entered into effect on 4 February 1997
Legal system
based on Roman-Dutch law and English common law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state:President Jacob ZUMA (since 9 May 2009); Executive Deputy President Kgalema MOTLANTHE (since 11 May 2009); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
Head of government:President Jacob ZUMA (since 9 May 2009); Executive Deputy President Kgalema MOTLANTHE (since 11 May 2009)
Cabinet:Cabinet appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:president elected by the National Assembly for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 6 May 2009 (next to be held in 2014)
Election results:Jacob ZUMA elected president; National Assembly vote - Jacob ZUMA 277, Mvume DANDALA 47, other 76
Legislative branch
bicameral Parliament consisting of the National Council of Provinces (90 seats; 10 members elected by each of the nine provincial legislatures for five-year terms; has special powers to protect regional interests, including the safeguarding of cultural and linguistic traditions among ethnic minorities) and the National Assembly (400 seats; members elected by popular vote under a system of proportional representation to serve five-year terms)
Elections:National Assembly and National Council of Provinces - last held on 22 April 2009 (next to be held in April 2014)
Election results:National Council of Provinces - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; National Assembly - percent of vote by party - ANC 65.9%, DA 16.7%, COPE 7.4%, IFP 4.6%, other 5.4%; seats by party - ANC 264, DA 67, COPE 30, IFP 18, other 21
Judicial branch
Constitutional Court; Supreme Court of Appeals; High Courts; Magistrate Courts
Political Parties and Leaders
African Christian Democratic Party or ACDP [Kenneth MESHOE]; African National Congress or ANC [Jacob ZUMA]; Congress of the People or COPE [Mosiuoa LEKOTA]; Democratic Alliance or DA [Helen ZILLE]; Freedom Front Plus or FF+ [Pieter MULDER]; Independent Democrats or ID [Patricia DE LILLE]; Inkatha Freedom Party or IFP [Mangosuthu BUTHELEZI]; Pan-Africanist Congress or PAC [Motsoko PHEKO]; United Christian Democratic Party or UCDP [Lucas MANGOPE]; United Democratic Movement or UDM [Bantu HOLOMISA]
Political pressure groups and leaders
Congress of South African Trade Unions or COSATU [Zwelinzima VAVI, general secretary]; South African Communist Party or SACP [Blade NZIMANDE, general secretary]; South African National Civics Organization or SANCO [Mlungisi HLONGWANE, national president]
note: note - COSATU and SACP are in a formal alliance with the ANC
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, BIS, C, CD, FAO, FATF, G-20, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MONUC, NAM, NSG, OPCW, Paris Club (associate), PCA, SACU, SADC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Johnny MOLOTO
Chancery:3051 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
Telephone:[1] (202) 232-4400
FAX:[1] (202) 265-1607
Consulate(s) general:Chicago, Los Angeles, New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Donald GIPS
Embassy:877 Pretorius Street, Pretoria
Mailing address:P. O. Box 9536, Pretoria 0001
Telephone:[27] (12) 431-4000
FAX:[27] (12) 342-2299
consulate(s) general: Cape Town, Durban, Johannesburg
Flag description
two equal width horizontal bands of red (top) and blue separated by a central green band that splits into a horizontal Y, the arms of which end at the corners of the hoist side; the Y embraces a black isosceles triangle from which the arms are separated by narrow yellow bands; the red and blue bands are separated from the green band and its arms by narrow white stripes; the flag colors do not have any official symbolism, but the Y stands for the "convergence of diverse elements within South African society, taking the road ahead in unity"; black, yellow, and green are found on the flag of the African National Congress, while red, white, and blue are the colors in the flags of the Netherlands and the UK, whose settlers ruled South Africa during the colonial era
note: the South African flag is the only national flag to display six colors as part of its primary design