Equatorial Guinea gained independence in 1968 after 190 years of Spanish rule. This tiny country, composed of a mainland portion plus five inhabited islands, is one of the smallest on the African continent. President Teodoro OBIANG NGUEMA MBASOGO has ruled the country since 1979 when he seized power in a coup. Although nominally a constitutional democracy since 1991, the 1996, 2002, and 2009 presidential elections - as well as the 1999 and 2004 legislative elections - were widely seen as flawed. The president exerts almost total control over the political system and has discouraged political opposition. Equatorial Guinea has experienced rapid economic growth due to the discovery of large offshore oil reserves, and in the last decade has become Sub-Saharan Africa's third largest oil exporter. Despite the country's economic windfall from oil production resulting in a massive increase in government revenue in recent years, there have been few improvements in the population's living standards.
Population
650,702 (July 2010 est.)
Country comparison to the world:166
Nationality
Noun:Equatorial Guinean(s) or Equatoguinean(s)
Adjective:Equatorial Guinean or Equatoguinean
Ethnic groups
Fang 85.7%, Bubi 6.5%, Mdowe 3.6%, Annobon 1.6%, Bujeba 1.1%, other 1.4% (1994 census)
Religions
nominally Christian and predominantly Roman Catholic, pagan practices
Languages
Spanish 67.6% (official), other 32.4% (includes French (official), Fang, Bubi) (1994 census)
Country Name
Conventional long form:Republic of Equatorial Guinea
Conventional short form:Equatorial Guinea
Local long form:Republica de Guinea Ecuatorial/Republique de Guinee equatoriale
Local short form:Guinea Ecuatorial/Guinee equatoriale
Former:Spanish Guinea
Government Type
republic
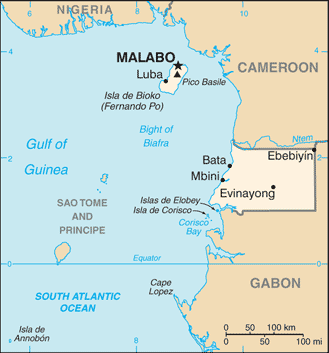
Capital
Name:Malabo
Geographic coordinates:3 45 N, 8 47 E
Time difference:UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
Administrative divisions
7 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia); Annobon, Bioko Norte, Bioko Sur, Centro Sur, Kie-Ntem, Litoral, Wele-Nzas
Independence
12 October 1968 (from Spain)
National Holiday
Independence Day, 12 October (1968)
Constitution
approved by national referendum 17 November 1991; amended January 1995
Legal system
partly based on Spanish civil law and tribal custom; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state:President Brig. Gen. (Ret.) Teodoro OBIANG NGUEMA MBASOGO (since 3 August 1979 when he seized power in a military coup)
Head of government:Prime Minister Ignacio Milan TANG (since 8 July 2008)
Cabinet:Council of Ministers appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:president elected by popular vote for a seven-year term (no term limits); election last held on 29 November 2009 (next to be held in 2016); prime minister and deputy prime ministers appointed by the president
Election results:Teodoro OBIANG NGUEMA MBASOGO reelected president; percent of vote - Teodoro OBIANG NGUEMA MBASOGO 95.8%, Placido Mico ABOGO 3.6%; elections marred by widespread fraud
Legislative branch
unicameral House of People's Representatives or Camara de Representantes del Pueblo (100 seats; members directly elected by popular vote to serve five-year terms)
Elections:last held on 4 May 2008 (next to be held in 2012)
Election results:percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PDGE 89, EC 10, CPDS 1
note: Parliament has little power since the constitution vests all executive authority in the president
Judicial branch
Supreme Tribunal
Political Parties and Leaders
Convergence Party for Social Democracy or CPDS [Placido MICO Abogo]; Democratic Party for Equatorial Guinea or PDGE [Teodoro OBIANG NGUEMA MBASOGO] (ruling party); Electoral Coalition or EC; Party for Progress of Equatorial Guinea or PPGE [Severo MOTO]; Popular Action of Equatorial Guinea or APGE [Avelino MOCACHE]; Popular Union or UP
Political pressure groups and leaders
ASODEGUE (Madrid-based pressure group for democratic reform); Global Witness (anti-corruption)
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, BDEAC, CEMAC, CPLP (associate), FAO, FZ, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OAS (observer), OIF, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WTO (observer)
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Purificacion ANGUE ONDO
Chancery:2020 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009
Telephone:[1] (202) 518-5700
FAX:[1] (202) 518-5252
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Alberto M. FERNANDEZ
Embassy:K-3, Carreterade Aeropuerto, al lado de Restaurante El Paraiso, Malabo; note - relocated embassy is opened for limited functions; inquiries should continue to be directed to the US Embassy in Yaounde, Cameroon
Mailing address:B.P. 817, Yaounde, Cameroon; US Embassy Yaounde, US Department of State, Washington, DC 20521-2520
Telephone:[237] 2220-1500
FAX:[237] 2220-1572
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of green (top), white, and red, with a blue isosceles triangle based on the hoist side and the coat of arms centered in the white band; the coat of arms has six yellow six-pointed stars (representing the mainland and five offshore islands) above a gray shield bearing a silk-cotton tree and below which is a scroll with the motto UNIDAD, PAZ, JUSTICIA (Unity, Peace, Justice); green symbolizes the jungle and natural resources, blue represents the sea that connects the mainland to the islands, white stands for peace, and red recalls the fight for independence