Present day Benin was the site of Dahomey, a prominent West African kingdom that rose in the 15th century. The territory became a French Colony in 1872 and achieved independence on 1 August 1960, as the Republic of Benin. A succession of military governments ended in 1972 with the rise to power of Mathieu KEREKOU and the establishment of a government based on Marxist-Leninist principles. A move to representative government began in 1989. Two years later, free elections ushered in former Prime Minister Nicephore SOGLO as president, marking the first successful transfer of power in Africa from a dictatorship to a democracy. KEREKOU was returned to power by elections held in 1996 and 2001, though some irregularities were alleged. KEREKOU stepped down at the end of his second term in 2006 and was succeeded by Thomas YAYI Boni, a political outsider and independent. YAYI has begun a high profile fight against corruption and has strongly promoted accelerating Benin's economic growth.
Population
9,056,010
Country comparison to the world: 90
note:estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2010 est.)
Nationality
Noun:Beninese (singular and plural)
Adjective: Beninese
Ethnic groups
Fon and related 39.2%, Adja and related 15.2%, Yoruba and related 12.3%, Bariba and related 9.2%, Peulh and related 7%, Ottamari and related 6.1%, Yoa-Lokpa and related 4%, Dendi and related 2.5%, other 1.6% (includes Europeans), unspecified 2.9% (2002 census)
Religions
Christian 42.8% (Catholic 27.1%, Celestial 5%, Methodist 3.2%, other Protestant 2.2%, other 5.3%), Muslim 24.4%, Vodoun 17.3%, other 15.5% (2002 census)
Languages
French (official), Fon and Yoruba (most common vernaculars in south), tribal languages (at least six major ones in north)
Country Name
Conventional long form:Republic of Benin
Conventional short form:Benin
Local long form: Republique du Benin
Local short form:Benin
Former:Dahomey
Government Type
republic
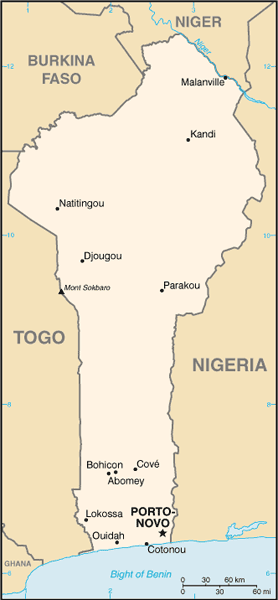
Capital
Name:Porto-Novo (official capital)
Geographic coordinates:6 29 N, 2 37 E
Time difference:UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
note:Cotonou (seat of government)
Administrative divisions
12 departments; Alibori, Atakora, Atlantique, Borgou, Collines, Kouffo, Donga, Littoral, Mono, Oueme, Plateau, Zou
Independence
1 August 1960 (from France)
National Holiday
National Day, 1 August (1960)
Constitution
adopted by referendum 2 December 1990
Legal system
based on French civil law and customary law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state: President Thomas YAYI Boni (since 6 April 2006); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
Head of government:President Thomas YAYI Boni (since 6 April 2006)
Cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); runoff election held on 19 March 2006 (next to be held in March 2011)
Election results: Thomas YAYI Boni elected president; percent of vote - Thomas YAYI Boni 74.5%, Adrien HOUNGBEDJI 25.5%
Legislative branch
unicameral National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (83 seats; members are elected by direct popular vote to serve four-year terms)
Elections: last held on 31 March 2007 (next to be held by March 2011)
Election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - FCBE 35, ADD 20, PRD 10, other and independents 18
Judicial branch
Constitutional Court or Cour Constitutionnelle; Supreme Court or Cour Supreme; High Court of Justice
Political Parties and Leaders
African Movement for Democracy and Progress or MADEP [Sefou FAGBOHOUN]; Alliance for Dynamic Democracy or ADD; Alliance of Progress Forces or AFP; Benin Renaissance or RB [Rosine SOGLO]; Democratic Renewal Party or PRD [Adrien HOUNGBEDJI]; Force Cowrie for an Emerging Benin or FCBE; Impulse for Progress and Democracy or IPD [Theophile NATA]; Key Force or FC [Lazare S HOU TO]; Movement for the People's Alternative or MAP [Olivier CAPO-CHICHI]; Rally for Democracy and Progress or RDP [Dominique HOUNGNINOU]; Social Democrat Party or PSD [Bruno AMOUSSOU]; Union for Democracy and National Solidarity or UDS [Sacca LAFIA]; Union for the Relief or UPR [Issa SALIFOU]
note: approximately 20 additional minor parties
Political pressure groups and leaders
Other:economic groups; environmentalists; political groups; teachers' unions and other educational groups
International organization participation
ACCT, ACP, AfDB, AU, ECOWAS, Entente, FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MONUC, NAM, OAS (observer), OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (regional), WAEMU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Cyrille Segbe OGUIN
Chancery:2124 Kalorama Road NW, Washington, DC 20008
Telephone:[1] (202) 232-6656
FAX:[1] (202) 265-1996
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador James A. KNIGHT
Embassy:Rue Caporal Bernard Anani, Cotonou
Mailing address:01 B. P. 2012, Cotonou
Telephone:[229] 21-30-06-50
FAX:[229] 21-30-03-84
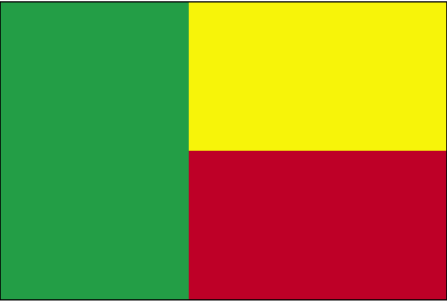
Flag description
two equal horizontal bands of yellow (top) and red (bottom) with a vertical green band on the hoist side; green symbolizes hope and revival, yellow wealth, and red courage
note: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia