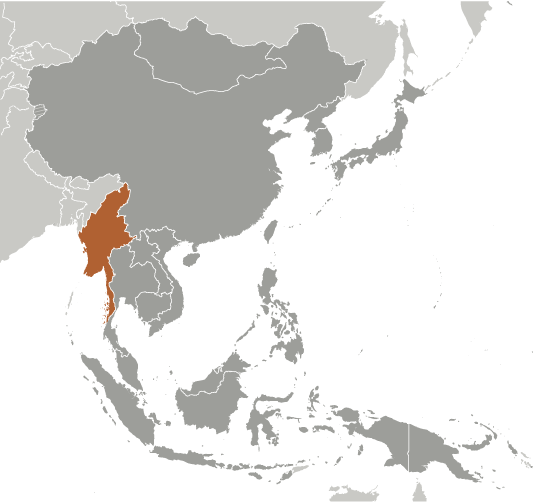
Britain conquered Burma over a period of 62 years (1824-1886) and incorporated it into its Indian Empire. Burma was administered as a province of India until 1937 when it became a separate, self-governing colony; independence from the Commonwealth was attained in 1948. Gen. NE WIN dominated the government from 1962 to 1988, first as military ruler, then as self-appointed president, and later as political kingpin. In September 1988, the military deposed NE WIN and established a new ruling junta. Despite multiparty legislative elections in 1990 that resulted in the main opposition party - the National League for Democracy (NLD) - winning a landslide victory, the junta refused to hand over power. NLD leader and Nobel Peace Prize recipient AUNG SAN SUU KYI, who was under house arrest from 1989 to 1995 and 2000 to 2002, was imprisoned in May 2003 and subsequently transferred to house arrest. After the ruling junta in August 2007 unexpectedly increased fuel prices, tens of thousands of Burmese marched in protest, led by prodemocracy activists and Buddhist monks. In late September 2007, the government brutally suppressed the protests, killing at least 13 people and arresting thousands for participating in the demonstrations. Since then, the regime has continued to raid homes and monasteries and arrest persons suspected of participating in the pro-democracy protests. The junta appointed Labor Minister AUNG KYI in October 2007 as liaison to AUNG SAN SUU KYI, who remains under house arrest and only recently gained the opportunity for limited communication with NLD leaders. Burma in early May 2008 was struck by Cyclone Nargis which official estimates claimed left over 80,000 dead and 50,000 injured. Despite this tragedy, the junta proceeded with its May constitutional referendum, the first vote in Burma since 1990, setting the stage for the 2010 parliamentary elections. AUNG SAN SUU KYI's house arrest was due to end in May 2009, but was extended for eighteen months after she was convicted for violating the terms of her house arrest.
Population
53,414,374
Country comparison to the world:24
note:estimates for this country take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2010 est.)
Nationality
Noun:Burmese (singular and plural)
Adjective: Burmese
Ethnic groups
Burman 68%, Shan 9%, Karen 7%, Rakhine 4%, Chinese 3%, Indian 2%, Mon 2%, other 5%
Religions
Buddhist 89%, Christian 4% (Baptist 3%, Roman Catholic 1%), Muslim 4%, animist 1%, other 2%
Languages
Burmese, minority ethnic groups have their own languages
Country Name
Conventional long form:Union of Burma
Conventional short form:Burma
Local long form:Pyidaungzu Myanma Naingngandaw (translated by the US Government as Union of Myanma and by the Burmese as Union of Myanmar)
Local short form: Myanma Naingngandaw
Former: Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma
note: since 1989 the military authorities in Burma have promoted the name Myanmar as a conventional name for their state; the US Government did not adopt the name, which is a derivative of the Burmese short-form name Myanma Naingngandaw
Government Type
military regime
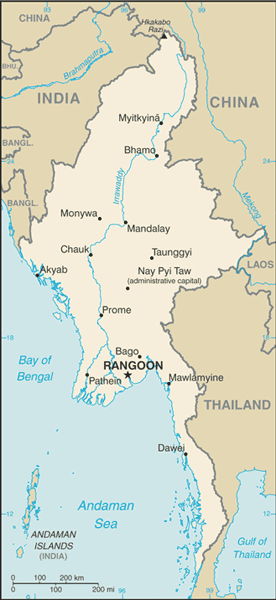
Capital
Name:Rangoon (Yangon)
Geographic coordinates:16 48 N, 96 09 E
Time difference:UTC+6.5 (11.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
note: Nay Pyi Taw is administrative capital
Administrative divisions
7 divisions (taing-myar, singular - taing) and 7 states* (pyi ne-myar, singular - pyi ne)
divisions: Ayeyarwady, Bago, Magway, Mandalay, Sagaing, Tanintharyi, Yangon
states: Chin, Kachin, Kayah, Kayin, Mon, Rakhine (Arakan), Shan
Independence
4 January 1948 (from the UK)
National Holiday
Independence Day, 4 January (1948); Union Day, 12 February (1947)
Constitution
3 January 1974; suspended since 18 September 1988; a constitution officially received 92.48% support in a flawed May 2008 referendum that most observers judged fell far short of international standards of free and fair elections; note - a new constitution is to take effect when a parliament is convened following elections planned for 2010
Legal system
based on English common law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state:Chairman of the State Peace and Development Council (SPDC) Sr. Gen. THAN SHWE (since 23 April 1992)
Head of government:Prime Minister Lt. Gen THEIN SEIN (since 24 October 2007)
Cabinet:Cabinet is overseen by the military regime that assumed power 18 September 1988 under the name State Law and Order Restoration Council (SLORC); changed in 1997 to SPDC
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:none
Legislative branch
a unicameral People's Assembly or Pyithu Hluttaw was elected in 1990 but was never seated; according to the terms of the constitution approved on 10 May 2008, a bicameral Pyidaungsu Hluttaw consisting of an upper house with a maximum of 224 seats and a lower house with a maximum of 440 seats will be selected in elections planned for 2010; 25% of both houses are to be reserved for appointed members of the military
Elections: last held on 27 May 1990, but the regime never allowed the Assembly to convene
Election results:percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NLD 392 (opposition), SNLD 23 (opposition), NUP 10 (pro-government), other 60
Judicial branch
remnants of the British-era legal system are in place, but there is no guarantee of a fair public trial; the judiciary is not independent of the executive
Political Parties and Leaders
National Democratic Force or NDF [THAN NYEIN]; National League for Democracy or NLD [AUNG SHWE, AUNG SAN SUU KYI] note: the party is defunct because it did not register for the 2010 election; National Unity Party or NUP [TUN YE]; Shan Nationalities League for Democracy or SNLD [HKUN HTUN OO]; Union Solidarity and Development Party or USDP [THEIN SEIN]; numerous smaller parties
Political pressure groups and leaders
Thai border: Ethnic Nationalities Council or ENC; Federation of Trade Unions-Burma or FTUB (exile trade union and labor advocates); National Coalition Government of the Union of Burma or NCGUB (self-proclaimed government in exile) ["Prime Minister" Dr. SEIN WIN] consists of individuals, some legitimately elected to the People's Assembly in 1990 (the group fled to a border area and joined insurgents in December 1990 to form parallel government in exile); National Council-Union of Burma or NCUB (exile coalition of opposition groups)
Inside Burma: Kachin Independence Organization or KIO; Karen National Union or KNU; Karenni National People's Party or KNPP; Union Solidarity and Development Association or USDA (pro-regime, a social and political mass-member organization) [HTAY OO, general secretary] note: the USDA became the Union Solidarity and Development Party in 2010; United Wa State Army or UWSA; 88 Generation Students (pro-democracy movement); several other Shan factions
International organization participation
ADB, APT, ARF, ASEAN, BIMSTEC, CP, EAS, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, ISO (correspondent), ITU, NAM, OPCW (signatory), SAARC (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires HAN THU - note: Burma does not have an ambassador to the United States
Chancery: 2300 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
Telephone:[1] (202) 332-3344
FAX:[1] (202) 332-4351
Consulate(s) general: none; Burma has a Mission to the UN in New York
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Charge d'Affaires Larry M. DINGER - note: The United States does not have an ambassador to Burma
Embassy: 110 University Avenue, Kamayut Township, Rangoon
Mailing address: Box B, APO AP 96546
Telephone:[95] (1) 536-509, 535-756, 538-038
FAX: [95] (1) 650-306
Flag description
red with a blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing 14, white, five-pointed stars encircling a cogwheel containing a stalk of rice; the colors stand for courage (red), peace (blue), and purity (white); the rice plant and cogwheel symbolize agriculture and industry repectively; the 14 stars represent the seven administrative divisions and seven states of the country