For centuries China stood as a leading civilization, outpacing the rest of the world in the arts and sciences, but in the 19th and early 20th centuries, the country was beset by civil unrest, major famines, military defeats, and foreign occupation. After World War II, the Communists under MAO Zedong established an autocratic socialist system that, while ensuring China's sovereignty, imposed strict controls over everyday life and cost the lives of tens of millions of people. After 1978, MAO's successor DENG Xiaoping and other leaders focused on market-oriented economic development and by 2000 output had quadrupled. For much of the population, living standards have improved dramatically and the room for personal choice has expanded, yet political controls remain tight. China since the early 1990s has increased its global outreach and participation in international organizations.
Locaion
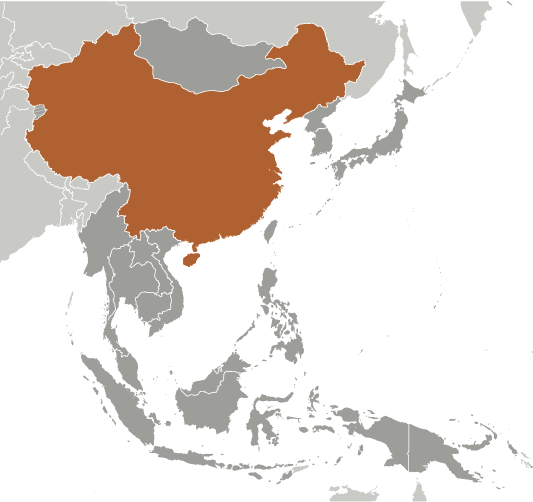
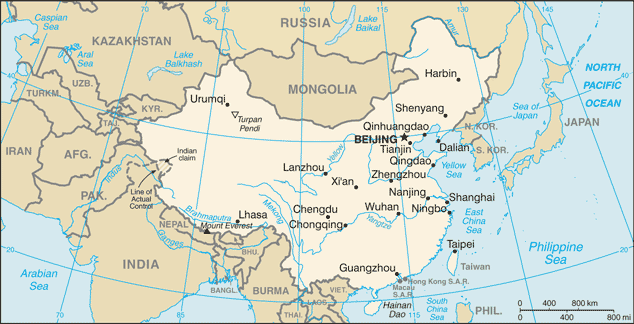
Eastern Asia, bordering the East China Sea, Korea Bay, Yellow Sea, and South China Sea, between North Korea and Vietnam
Geographic Co ordinates
35 00 N, 105 00 E
Land Boundries
Total:22,117 km
Border countries:Afghanistan 76 km, Bhutan 470 km, Burma 2,185 km, India 3,380 km, Kazakhstan 1,533 km, North Korea 1,416 km, Kyrgyzstan 858 km, Laos 423 km, Mongolia 4,677 km, Nepal 1,236 km, Pakistan 523 km, Russia (northeast) 3,605 km, Russia (northwest) 40 km, Tajikistan 414 km, Vietnam 1,281 km
regional borders: Hong Kong 30 km, Macau 0.34 km
Geography - note
world's fourth largest country (after Russia, Canada, and US); Mount Everest on the border with Nepal is the world's tallest peak
Population
1,330,141,295 (July 2010 est.)
Country comparison to the world:1
Nationality
Noun:Chinese (singular and plural)
Adjective:Chinese
Ethnic groups
Han Chinese 91.5%, Zhuang, Manchu, Hui, Miao, Uyghur, Tujia, Yi, Mongol, Tibetan, Buyi, Dong, Yao, Korean, and other nationalities 8.5% (2000 census)
Religions
Daoist (Taoist), Buddhist, Christian 3%-4%, Muslim 1%-2%
note: officially atheist (2002 est.)
Languages
Standard Chinese or Mandarin (Putonghua, based on the Beijing dialect), Yue (Cantonese), Wu (Shanghainese), Minbei (Fuzhou), Minnan (Hokkien-Taiwanese), Xiang, Gan, Hakka dialects, minority languages (see Ethnic groups entry)
Country Name
Conventional long form:People's Republic of China
Conventional short form: China
Local long form:Zhonghua Renmin Gongheguo
Local short form:Zhongguo
abbreviation: PRC
Government Type
Communist state
Capital
Name:Beijing
Geographic coordinates:39 55 N, 116 23 E
Time difference:UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
note: despite its size, all of China falls within one time zone; many people in Xinjiang Province observe an unofficial "Xinjiang timezone" of UTC+6, two hours behind Beijing
Administrative divisions
23 provinces (sheng, singular and plural), 5 autonomous regions (zizhiqu, singular and plural), and 4 municipalities (shi, singular and plural)
provinces: Anhui, Fujian, Gansu, Guangdong, Guizhou, Hainan, Hebei, Heilongjiang, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangsu, Jiangxi, Jilin, Liaoning, Qinghai, Shaanxi, Shandong, Shanxi, Sichuan, Yunnan, Zhejiang; (see note on Taiwan)
autonomous regions: Guangxi, Nei Mongol, Ningxia, Xinjiang Uygur, Xizang (Tibet)
municipalities: Beijing, Chongqing, Shanghai, Tianjin
note: China considers Taiwan its 23rd province; see separate entries for the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau
Independence
221 BC (unification under the Qin Dynasty); 1 January 1912 (Qing Dynasty replaced by the Republic of China); 1 October 1949 (People's Republic of China established)
National Holiday
Anniversary of the founding of the People's Republic of China, 1 October (1949)
Constitution
most recent promulgation 4 December 1982 with amendments in 1988, 1993, 2004
Legal system
based on civil law system; derived from Soviet and continental civil code legal principles; legislature retains power to interpret statutes; constitution ambiguous on judicial review of legislation; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state: President HU Jintao (since 15 March 2003); Vice President XI Jinping (since 15 March 2008)
Head of government:Premier WEN Jiabao (since 16 March 2003); Executive Vice Premier LI Keqiang (17 March 2008), Vice Premier HUI Liangyu (since 17 March 2003), Vice Premier ZHANG Deijiang (since 17 March 2008), and Vice Premier WANG Qishan (since 17 March 2008)
Cabinet:State Council appointed by National People's Congress
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:president and vice president elected by National People's Congress for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); elections last held on 15-17 March 2008 (next to be held in mid-March 2013); premier nominated by president, confirmed by National People's Congress
Election results:HU Jintao elected president by National People's Congress with a total of 2,963 votes; XI Jinping elected vice president with a total of 2,919 votes
Legislative branch
unicameral National People's Congress or Quanguo Renmin Daibiao Dahui (2,987 seats; members elected by municipal, regional, and provincial people's congresses, and People's Liberation Army to serve five-year terms)
Elections: last held in December 2007-February 2008 (date of next election to be held in late 2012 to early 2013)
Election results:percent of vote - NA; seats - 2,987
note: only members of the CCP, its eight allied parties, and sympathetic independent candidates are elected
Judicial branch
Supreme People's Court (judges appointed by the National People's Congress); Local People's Courts (comprise higher, intermediate, and basic courts); Special People's Courts (primarily military, maritime, railway transportation, and forestry courts)
Political Parties and Leaders
Chinese Communist Party or CCP [HU Jintao]; eight registered small parties controlled by CCP
Political pressure groups and leaders
no substantial political opposition groups exist
International organization participation
ADB, AfDB (nonregional member), APEC, APT, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), BIS, CDB, CICA, EAS, FAO, FATF, G-20, G-24 (observer), G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAIA (observer), MIGA, MINURSO, MONUC, NAM (observer), NSG, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), SCO, SICA (observer), UN, UN Security Council, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNITAR, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNMIT, UNOCI, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador ZHANG Yesui
Chancery:3505 International Place NW, Washington, DC 20008
Telephone:[1] (202) 495-2000
FAX:[1] (202) 495-2190
Consulate(s) general:Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Jon M. HUNTSMAN, Jr.
Embassy:55 An Jia Lou Lu, 100600 Beijing
Mailing address:PSC 461, Box 50, FPO AP 96521-0002
Telephone: [86] (10) 8531-3000
FAX:[86] (10) 8531-3300
consulate(s) general: Chengdu, Guangzhou, Shanghai, Shenyang, Wuhan
Flag description
red with a large yellow five-pointed star and four smaller yellow five-pointed stars (arranged in a vertical arc toward the middle of the flag) in the upper hoist-side corner; the color red represents revolution, while the stars symbolize the four social classes - the working class, the peasantry, the urban petty bourgeoisie, and the national bourgeoisie (capitalists) - united under the Communist Party of China