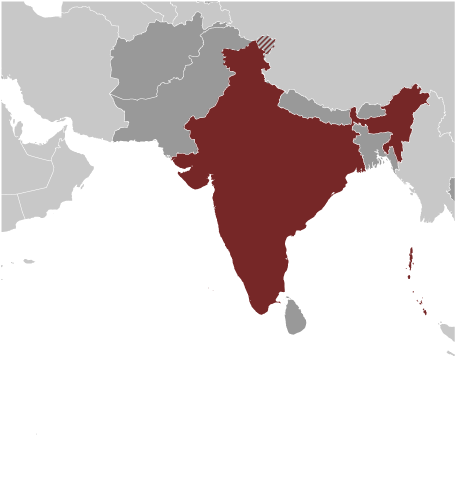
The Indus Valley civilization, one of the world's oldest, flourished during the 3rd and 2nd millennia B.C. and extended into northwestern India. Aryan tribes from the northwest infiltrated onto the Indian subcontinent about 1500 B.C.; their merger with the earlier Dravidian inhabitants created the classical Indian culture. The Maurya Empire of the 4th and 3rd centuries B.C. - which reached its zenith under ASHOKA - united much of South Asia. The Golden Age ushered in by the Gupta dynasty (4th to 6th centuries A.D.) saw a flowering of Indian science, art, and culture. Islam spread across the subcontinent over a period of 700 years. In the 10th and 11th centuries, Turks and Afghans invaded India and established the Delhi Sultanate. In the early 16th century, the Emperor BABUR established the Mughal Dynasty which ruled India for more than three centuries. European explorers began establishing footholds in India during the 16th century. By the 19th century, Great Britain had become the dominant political power on the subcontinent. The British Indian Army played a vital role in both World Wars. Nonviolent resistance to British rule, led by Mohandas GANDHI and Jawaharlal NEHRU, eventually brought about independence in 1947. Communal violence led to the subcontinent's bloody partition, which resulted in the creation of two separate states, India and Pakistan. The two countries have fought three wars since independence, the last of which in 1971 resulted in East Pakistan becoming the separate nation of Bangladesh. India's nuclear weapons tests in 1998 caused Pakistan to conduct its own tests that same year. In November 2008, terrorists allegedly originating from Pakistan conducted a series of coordinated attacks in Mumbai, India's financial capital. Despite pressing problems such as significant overpopulation, environmental degradation, extensive poverty, and widespread corruption, rapid economic development is fueling India's rise on the world stage.
Population
1,173,108,018 (July 2010 est.)
Country comparison to the world:2
Nationality
Noun:Indian(s)
Adjective:Indian
Ethnic groups
Indo-Aryan 72%, Dravidian 25%, Mongoloid and other 3% (2000)
Religions
Hindu 80.5%, Muslim 13.4%, Christian 2.3%, Sikh 1.9%, other 1.8%, unspecified 0.1% (2001 census)
Languages
Hindi 41%, Bengali 8.1%, Telugu 7.2%, Marathi 7%, Tamil 5.9%, Urdu 5%, Gujarati 4.5%, Kannada 3.7%, Malayalam 3.2%, Oriya 3.2%, Punjabi 2.8%, Assamese 1.3%, Maithili 1.2%, other 5.9%
note: English enjoys the status of subsidiary official language but is the most important language for national, political, and commercial communication; Hindi is the most widely spoken language and primary tongue of 41% of the people; there are 14 other official languages: Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil, Urdu, Gujarati, Malayalam, Kannada, Oriya, Punjabi, Assamese, Kashmiri, Sindhi, and Sanskrit; Hindustani is a popular variant of Hindi/Urdu spoken widely throughout northern India but is not an official language (2001 census)
Country Name
Conventional long form:Republic of India
Conventional short form:India
Local long form:Republic of India/Bharatiya Ganarajya
Local short form:India/Bharat
Government Type
federal republic
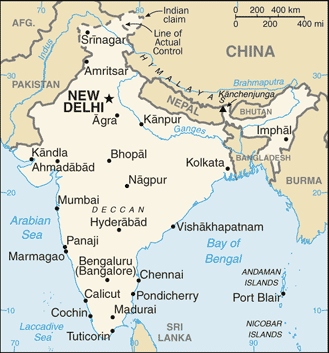
Capital
Name:New Delhi
Geographic coordinates:28 36 N, 77 12 E
Time difference:UTC+5.5 (10.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
Administrative divisions
28 states and 7 union territories*; Andaman and Nicobar Islands*, Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chandigarh*, Chhattisgarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli*, Daman and Diu*, Delhi*, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep*, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Orissa, Puducherry*, Punjab, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal
Independence
15 August 1947 (from the UK)
National Holiday
Republic Day, 26 January (1950)
Constitution
26 January 1950; amended many times
Legal system
based on English common law; judicial review of legislative acts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; separate personal law codes apply to Christians, Hindus, and Muslims
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
Chief of state:President Pratibha PATIL (since 25 July 2007); Vice President Hamid ANSARI (since 11 August 2007)
Head of government:Prime Minister Manmohan SINGH (since 22 May 2004)
Cabinet:Cabinet appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website)
Elections:president elected by an electoral college consisting of elected members of both houses of Parliament and the legislatures of the states for a five-year term (no term limits); election last held in July 2007 (next to be held in July 2012); vice president elected by both houses of Parliament for a five-year term; election last held in August 2007 (next to be held August 2012); prime minister chosen by parliamentary members of the majority party following legislative elections; election last held April - May 2009 (next to be held no later than May 2014)
Election results: Pratibha PATIL elected president; percent of vote - Pratibha PATIL 65.8%, Bhairon Singh SHEKHAWAT - 34.2%
Legislative branch
bicameral Parliament or Sansad consists of the Council of States or Rajya Sabha (a body consisting of not more than 250 members up to 12 of whom are appointed by the president, the remainder are chosen by the elected members of the state and territorial assemblies; members serve six-year terms) and the People's Assembly or Lok Sabha (545 seats; 543 members elected by popular vote, 2 appointed by the president; members serve five-year terms)
Elections:People's Assembly - last held in five phases on 16, 22-23, 30 April and 7, 13 May 2009 (next must be held by May 2014)
Election results:People's Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - INC 206, BJP 116, SP 23, BSP 21, JD (U) 20, AITC 19, DMK 18, CPI-M 16, BJD 14, SS 11, AIADMK 9, NCP 9, other 61, vacant 2
Judicial branch
Supreme Court (one chief justice and 25 associate justices are appointed by the president and remain in office until they reach the age of 65 or are removed for "proved misbehavior")
Political Parties and Leaders
All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam or AIADMK [J. JAYALALITHAA]; All India Trinamool Congress or AITC [Mamata BANERJEE]; Bahujan Samaj Party or BSP [MAYAWATI]; Bharatiya Janata Party or BJP [Nitin GADKARI]; Biju Janata Dal or BJD [Naveen PATNAIK]; Communist Party of India or CPI [B. BARDHAN]; Communist Party of India-Marxist or CPI-M [Prakash KARAT]; Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam or DMK [Kalaignar M.KARUNANIDHI]; Indian National Congress or INC [Sonia GANDHI]; Janata Dal (United) or JD(U) [Sharad YADAV]; Left Front (an alliance of Indian leftist parties); Nationalist Congress Party or NCP [Sharad PAWAR]; Rashtriya Lok Dal or RLD [Ajit SINGH]; Samajwadi Party or SP [Mulayam Singh YADAV]; Shiromani Akali Dal or SAD [Parkash Singh BADAL]; Shiv Sena or SS [Bal THACKERAY]; Telugu Desam Party or TDP [Chandrababu NAIDU]; note - India has dozens of national and regional political parties; only parties or coalitions with four or more seats in the People's Assembly are listed
Political pressure groups and leaders
All Parties Hurriyat Conference in the Kashmir Valley (separatist group); Bajrang Dal (religious organization); National Socialist Council of Nagaland in the northeast (separatist group); Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh [Mohan BHAGWAT] (religious organization); Vishwa Hindu Parishad [Ashok SINGHAL] (religious organization)
Other: numerous religious or militant/chauvinistic organizations; various separatist groups seeking greater communal and/or regional autonomy
International organization participation
ADB, AfDB (nonregional member), ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), BIMSTEC, BIS, C, CD, CERN (observer), CICA, CP, EAS, FAO, G-15, G-20, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, LAS (observer), MIGA, MONUC, NAM, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC, SACEP, SCO (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNITAR, UNMIS, UNMIT, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US
Chief of mission:Ambassador Meera SHANKAR
Chancery: 2107 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008; note - Consular Wing located at 2536 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
Telephone:[1] (202) 939-7000
FAX: [1] (202) 265-4351
Consulate(s) general:Chicago, Houston, New York, San Francisco
Diplomatic representation from the US
Chief of mission: Ambassador Timothy J. ROEMER
Embassy:Shantipath, Chanakyapuri, New Delhi 110021
Mailing address:use embassy street address
Telephone:[91] (011) 2419-8000
FAX:[91] (11) 2419-0017
consulate(s) general: Chennai (Madras), Hyderabad; Kolkata (Calcutta), Mumbai (Bombay)
Flag description
three equal horizontal bands of saffron (subdued orange) (top), white, and green, with a blue chakra (24-spoked wheel) centered in the white band
note: similar to the flag of Niger, which has a small orange disk centered in the white band